Difference between Polyester staple fiber and Polyester filament yarn
In the present day, Polyester is commonly used in the textile industry, which is divided into two types: polyester staple fiber and polyester filament yarn. The major differences between polyester staple and polyester filament yarn are length, classification and characteristics.
The first difference between polyester staple fiber and polyester filament yarn is length. Although polyester staple fiber is short fiber, the length varies from a few centimeters to 10 centimeters. On the other hand, polyester filament yarn is a continuous fiber with a long yarn that starts from 1,000 meters winding into a group.
In addition, there are differences in classification.
Polyester staple fiber is primarily used in spinning to produce spun yarn, while polyester filament yarn is divided into three categories.
- Pre Oriented Yarn (POY) is straight-oriented and is used in post-processing production to produce stretch fibers such as Drawn Textured Yarn.
- FDY (full draft yarn) and Fully Drawn Yarn (FDY) are primarily used as weft and weaves for making high-strength fabrics and textiles. However, FDY can also be knitted or woven with other filament yarns to produce various fabrics.
- Drawn Textured Yarn (DTY) has the advantages of short flow and high-efficiency good quality. Three combinations of intermingling points are Non-Intermingle (NIM), Semi-Intermingle (SIM), and High-Intermingle (HIM).
Different Concepts
1. Polyester Filament: Polyester filament is produced from polyester, specifically through the polymerization of either pure terephthalic acid (PTA) or dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) combined with ethylene glycol (MEG) using either esterification or transesterification followed by polycondensation. This type of fiber is created through a spinning process and subsequent post-treatment. Fabrics made from filament exhibit a shiny, smooth texture akin to nylon. In contrast, staple fibers are designed to blend with other fibers such as cotton. Polyester filament is characterized by its continuous length, often extending for kilometers, and it is typically wound into a ball. Conversely, polyester staple fibers are shorter, ranging from a few centimeters to over ten centimeters in length. Filament denotes continuous fibers, resembling silk and other synthetic fibers, which produce long tows during the silk-making process. Generally, multiple single filaments are combined to create the fabric, resulting in a smooth and shiny surface, making it suitable for summer clothing.
Polyester filament is a durable continuous fiber known for its strength and versatility. DTY textured filament (draw textured yarn) is produced through the processing of POY (partially oriented yarn) and undergoes stretching and crimping processes to enhance the yarn’s strength, volume, and softness.
This material has a variety of applications including fabrics, knits, apparel, ribbons, labels, sporting goods, decorative items such as cushions and duvets, tennis fabrics, car seats, and zippers.
2. Staple Fibers: Staple fibers are produced by cutting polyester into shorter bundles of fibers. These fibers can also be derived from natural materials such as cotton, wool, and hemp, typically measuring from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters in length. Staple fibers may also be cut from longer filaments. To create continuous yarns suitable for weaving, these fibers must undergo twisting and spinning. Fabrics composed of short fibers possess a soft, plump, and fluffy appearance, making them ideal for use in autumn and winter apparel.
Different Characteristics
1. Polyester Filament: This type of fiber is recognized for its high strength, excellent heat resistance (usable within the range of -70°C to 170°C), superior elasticity comparable to that of wool, and notable wear resistance, ranking just below nylon. Additionally, polyester demonstrates good water absorption properties.
2. Staple Fibers: Polyester staple fibers exhibit wear resistance that is second only to nylon among synthetic fibers. However, they possess lower water absorption and moisture regain, which affects their insulation performance. The reduced water absorption also contributes to increased static electricity generated through friction, resulting in less favorable dyeing characteristics.
Different Uses
1. Polyester Filament: Polyester filament serves as a versatile clothing fiber widely utilized in a variety of apparel and decorative materials. Additionally, it finds applications in industrial settings, including conveyor belts, tents, canvas, cables, and fishing nets.
2. Staple Fibers: These fibers are primarily employed in the cotton spinning industry, whether spun alone or in combination with materials such as cotton, viscose fibers, hemp, wool, and vinylon. The resulting yarn is predominantly used for clothing production, as well as in home decoration fabrics, packaging materials, filling materials, and thermal insulation products.
Different Production Process
1.1 Polyester staple fibers are produced by feeding polyester (PET) melt into the spinning machine, or by drying and melting polyester chips into the spinning machine, and then by clustering, drawing, setting, crimping, cutting, packaging, to obtain polyester staple fibers.
1.2 Polyester chemical yarn is produced by drying and melting polyester chips into the spinning machine, or by feeding polyester melt into the spinning machine. After different post-processing, the drawing twist yarn, the drawing textured yarn, the air textured yarn and the full draft yarn are obtained.
Polyester staple fibers and polyester filaments are flammable. Heat carrier biphenyl is flammable, explosive and toxic.
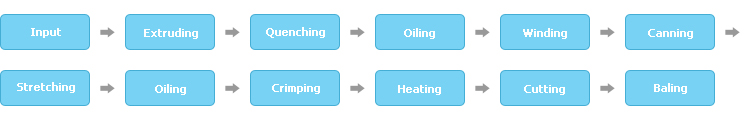
Polyester Staple fiber production process
The base material, which comes in chips, is melted in an extruder before being quantified in a gear pump and transferred to a nozzle. Polymers that pass through the nozzle are cooled and solidified in a spinning tank, and end up in a fiber form (semi-finished product). Fiber released from multiple spinning tanks is lubricated and gathered before being wound by a gear wheel and placed in cans. Fiber placed in cans is given various properties through a stretching process, in which fiber is stretched at various roller speeds designed to endow different degrees of rigidity and elasticity.
The fiber is again lubricated for enhanced quality and to facilitate the processes that follow. A crimping process takes place to give the fiber various properties, including bulk and mixability. Moisture and lubricant on the fiber is dried off in a heat dryer. The fiber is then cut into required lengths and end up in a bale form. The fiber is then compressed, packaged, and stored for factory release when ordered.
Polyester staple fiber production process
The production of polyester fibers consists of two main stages: polycondensation and melt spinning. The primary raw materials for polyester fibers include toluene, xylene, and ethylene, which are derived from petroleum, coal, or natural gas. Through chemical processing, these materials yield terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate and ethylene glycol. The polycondensation of these substances results in synthetic fiber polymers. Melt spinning subsequently produces the cooling filament, which undergoes additional processing steps, including clustering, drawing, crimping, heat setting, and cutting, to yield the finished product.
- Slice Preparation: The initial stage of the production process involves the preparation of polyester slices. Polyester chips are produced from raw polyester materials, utilizing processes such as melting, extrusion, stretching, and cutting.
- Dry Spinning: The chips are placed into a melt viscosity control device, where they are heated to a molten state. Following this, the melted material is filtered, pressurized, and extruded through a nozzle via spinning holes. High-speed airflow stretches the molten material into fibers, which are then cooled and directed into a take-up tray.
- Liquid Method Spinning: In this method, the chips are combined with mixed solvents, and a high-speed rotating centrifuge separates the solvents from the wet fibers using centrifugal force. The wet fibers are then dried with hot air to produce polyester staple fiber.
- Fiber Stretching: The collected wet fibers are subject to directional stretching to enhance their strength and improve the uniformity of the fiber cross-section. During this phase, the stretching ratio and speed are carefully controlled to optimize the mechanical properties of the fibers.
- Cutting: The stretched fibers are processed through a cutting machine to achieve the desired length. The specific cutting length is determined based on the intended application of the fibers.
- Heat-Setting: Polyester staple fibers undergo a heat-setting process to provide them with resilience and shape stability. During this procedure, the fibers are subjected to hot air at elevated temperatures, allowing for rapid heating and a controlled holding period. Adjustments to temperature and duration facilitate the desired heat-setting effect.
- Thread Lowering: The heat-set polyester staple fibers pass through a thread lowering mechanism, which establishes a predetermined thread density. Subsequently, the fibers are wound into rolls using a winding machine.
- Finished Product Inspection: Upon completion of production, the polyester staple fiber undergoes rigorous inspection to assess physical properties, including gloss, breaking strength, and elongation at break. Additionally, a visual inspection is conducted to ensure the fibers meet established product standards.
How to Achieve Safe Production of Polyester Staple Fiber
- Controlling chip drying and melt spinning properly to promote smooth operation.
- Screw extrusion melt spinning is heated by biphenyl heat carrier. When the temperature of biphenyl rises, it needs to exhaust. The exhaust should be slow so as not to take the biphenyl out. When exhausting, it is strictly forbidden to approach the open fire and not to be discharged into the room, so as to avoid ignition and poisoning.
- The temperature of the post is high, so we should do a good job of cooling the Department of Defense.
- The winding speed of the winding machine is very high. It is easy to bring the hook into the winding machine by slight carelessness in operation, which causes the flying hook to injure people. Therefore, it is necessary to educate the operator to concentrate on the manipulation and to stand in a favorable safe position so as to avoid the injury of the flying hook. When winding the scrap wire on the scrap wire roller, if there are several bunches of wire on the roller, then hold the original bundle with one hand when winding the wire, so as not to roll the hook and cause flying hook. When cutting scrap silk on scrap silk roller, the brake device should be stepped on by foot, and the scrap silk should be cut with knotting knife after it is stopped.
- When lifting or lowering the cluster rack, no people are allowed to stand under it.
- When dealing with draft wrapping rolls, it is necessary to slow down or stop them. When hooking wire, concentrate on hooking wire at the exit to prevent hooking hand.
- Pay attention to the oil can not spill, once spilled out of the ground to wash in time to prevent slippage.
- When the cutter is starting and lifting, the hand holds the wire head and feeds it into the cutter hook wheel. If it is not properly coordinated, it is easy to have the hand not left, and the console has been turned on, and the hand is brought in, resulting in the cutter accident. Therefore, the operation of the cutter must be closely coordinated and turned on after the hand leaves.
- In the process of packing, the main pressure cover wrapping cloth should be put on when the machine stops, and then the main pressure cover should be raised. Never use the main pressure cover to cover the wrapping cloth when lifting the pressure cover, in case of squeezing hands.
- We should do a good job in the fire prevention of the fibre warehouse
- No “shawl hair” on duty. Lesbians should cover their hair in their work caps, and they are not allowed to wear high-heeled shoes or hand ornaments.
- Workshop is noisy, pay attention to personal protection.
- Maintenance workers should wear protective clothing to prevent scalds when they go to high temperature positions for inspection.
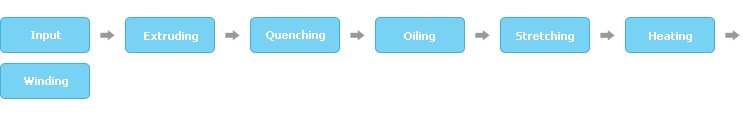
Polyester Filament production process
Dried chips are melted in an extruder before being quantified in a gear pump and transferred to a nozzle. Polymers are pushed through the tiny holes in the nozzle by heat and pressure, resulting in fiber, which is then cooled by cold air or water.
A single filament of mono filament is stretched to achieve various rigidity and elasticity. Stretching takes place at various roller speeds.The filament is then heat-treated to seal in the properties. Set amounts of filament are wound around bobbins and packaged. During packaging, a quality inspection takes place to set aside defective products.
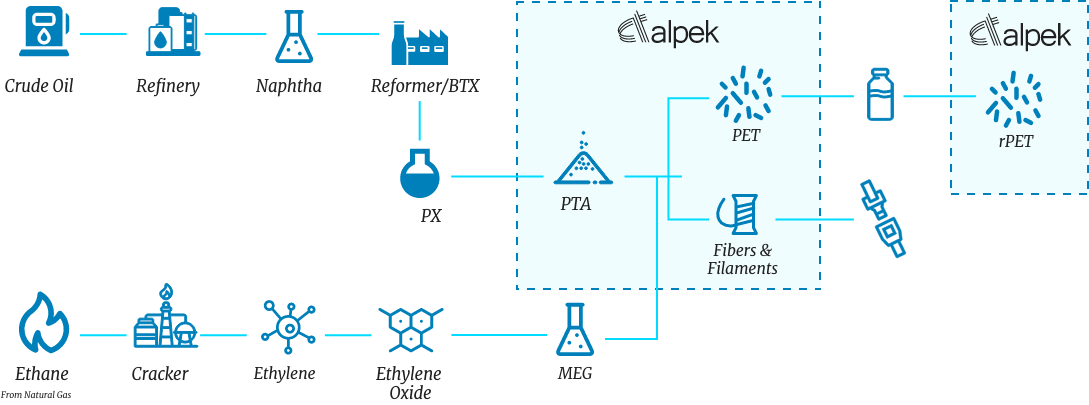
POLYESTER VALUE CHAIN
As part of the Polyester value chain, we manufacture Purified Terephthalic Acid (PTA) by oxidizing Paraxylene (Px). From there we make Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) by combining PTA with Monoethylene Glycol (MEG). Finally we transform recovered PET bales into recycled PET (rPET) flake and pellet.
Non-woven production process
Step 1: Choice of material: Nylon, Polyester, Polyolefin (PE/PP, PE/PET), Polypropylene
Step 2: Web formation: Carding, Air laid, Wet laid (Spunbond, Melt Blown, Flash spun)
Step 3: Web bonding: Needle punch, Spunlace, Thermal bond, Hot air-throught bond (Chemical bond, stitch bond)
Step 4: After treatment: Dyeing, Treatment