Basic Information about Low Melt Staple Fiber
Low melting fiber is a bi-component fiber known for its strong bonding properties, often used in the spinning of durable yarns. It is valued for its thermal bonding capabilities, making it a popular choice in industries such as automotive and construction for insulation. This fiber can be blended with solid recycled material or solid polyester fibers for applications such as car molding. Its easy bonding and high elasticity properties make it ideal for producing interior car parts, mattresses, medical goods, and more.
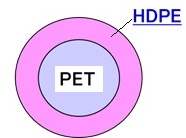
Low Melting Fiber is composed of a sheath/core structure, with the sheath polymer having a lower melting point than the core polymer. This fiber offers benefits such as low melting point, durability, and high bonding strength, making it versatile for various applications. It is commonly blended with other fibers to create padding, interlining, high-quality mattresses, and sanitary and medical products. The unique advantages of low melting fiber make it a sought-after material worldwide.
Low melt fibers utilize sheath-core fibers that melt at high temperatures and bond with other fibers to provide excellent matrix stability and handling characteristics. Low melt fibers also enhance cushioning product quality and are more compatible with the environment.
Use: Mattress of bed, seat cushions
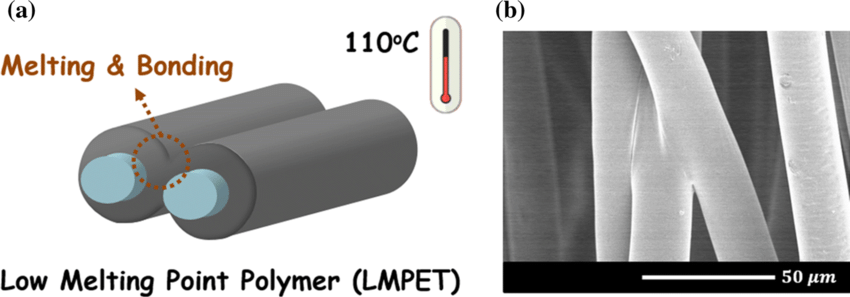
Low melting Fiber can be melted at a lower temperature (100~200°C), making it possible to be bonded with other fibers without any harmful adhesives, compared with normal polyester fiber is melted at a higher temperature of more than 280°C. This property contributes to environmental conservation by generating less carbon dioxide and heat. Its applications vary from automotive car interiors (door trims, ceiling materials, headliners, etc.), to furniture, construction, and industrial use.
Huvis, the largest polyester company in Korea was launched in 2000 when SK Chemical and Samyang Corporation separated their fabric divisions, which led the polyester business for the past 30 years. Currently, the world’s largest LM fiber company produces about 40% low melting Fiber in the world and exports to 80 countries, including Europe, North America, growing by 8% annually.
Currently, there are no Vietnam suppliers of low melt fibers. But we can supply this low melt fiber and mix it with our current products to load into containers for export.
What is Bicomponent fiber?
By blending two kinds of polymers, new fibers are made which own every characteristic of each polymer.
Bi-Component binder fibers with high-performance ability.
Bicomponent fibers have various types that suitable for heat-bonded nonwoven fabrics, dependent on their purpose and application (carding, wetlaid, airlaid).
Among other advantages such as soft touch, durable performance, process stability, and high speed, the bicomponent fibers have different melting points depending on the raw material used and make it possible to achieve a significantly higher material strength.
The first specific characteristic of Bi-Component fibers is the difference between the melting point of two polymers that causes one of these polymers to play as glue for sticking two fibers.
The best-known Bi-Component Fibers are: (PET-PET, PET-PP, PET-PE, PP-PE)
The following options/combinations are available:
- Polyester/Polyethylene
- Polyester/PBT
- Polyester/Co-polyester
- PLA / Co-PLA
- PLA / PBS
Fineness: 0.9 – 9 dtex
Cut length: 3-80 mm
Fiber shape: Round
Applications:
1- Health and Medical Industry
2- Hospital Bedsheets and Wearing
3- Industrial filtration
4- Food Packaging (tea Bag)
5- Automotive Industry