What is polyester fiber?
Polyester fiber or polyester staple fiber (PSF) has extensive applications in spinning, weaving, and non-woven processes, predominantly employed for filling pillows and sofas with fibers. Polyester fiber or polyester staple fiber comes in varying degrees of luster, categorized as Semi Dull or Bright. Additionally, through the integration of color master-batch, Polyester fiber or polyester staple fiber can be dyed to achieve Optical White, Black, and various other colors. Renowned for its lightweight nature, Polyester fiber or polyester staple fiber is wrinkle-resistant and exhibits durability against light exposure and weather conditions, demonstrating resilience even in harsh climates.
Polyester fiber (PSF) is a synthetic fiber composed entirely of polyester, derived from recycled PET bottle flakes. PSF crafted from PET chips is termed as Virgin PSF, while PSF manufactured from recycled PET flakes is referred to as Recycled PSF. This versatile material finds extensive applications across textile, automotive, and furniture sectors.





- PET Fiber
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is the main polyester used in fiber production. PET is a semi-crystalline polymer, and the physical parameters of PET have been summarized in the table below. PET fiber is the most produced synthetic fiber in the world. PET fiber has high strength, good elasticity, excellent heat setting performance, good heat resistance, acid and alkali resistance and other properties.
| Crystal habit | Triclinic: one polymer chain per unit cell |
| Cell parameters | a = 0.444 nm; b = 0.591 nm; c = 1.067 nm, α = 100 degrees; β= 117 degrees; γ = 112 degrees |
| Cell density | 1.52 g/cm3 |
| Tm (DSC) | 260°C ~ 265°C |
| ΔHf | 140 J/g; 33.5 cal/g |
| Tg (solid chip) | 79°C (DSC) |
| Tg (drawn fiber) | 120°C (dynamic loss) |
| Specific gravity | 1.33 (amorphous, undrawn), 1.39 (crystalline drawn fiber) |
- Other Polyester Fibers
Other polyester fibers include polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT), poly-1,4-cyclohexanedimethyl terephthalate, Polyethylene 2,6-naphthalate fibers, and various modified polyester-based fibers. Among them, PBT fiber has excellent resilience, mildew and moth resistance, good curling elasticity, antistatic property and dyeing property. PTT fiber has excellent dimensional stability, stain resistance, wrinkle resistance, abrasion resistance and easy dyeing.
Structure
- Chemical Structure
Polyester fibers are synthetic fibers composed of polyester linear macromolecules produced by polycondensation of diols and dibasic acids or ω-hydroxy acids. The chemical structure of polyester fibers involves two aspects, one is the molecular level (molecular chain and its structure), and the other is the supramolecular level (crystalline and amorphous regions).
PET fibers have rigid benzene rings in their backbone. A single chain contains the sequence of six aliphatic groups (-CO-O-CH2-CH2-O-CO-). The practical coplanar arrangement of benzene rings, carboxyl groups and aliphatic molecular groups in adjacent chains allows for side-by-side alignment. The molecular chain structure of PET is shown in the figure. Therefore, the PET macromolecular chain shows great rigidity, which makes the PET fiber show some inherent characteristics, such as higher melting point, higher rigidity and higher strength of the fiber.
Chemical structure of PET
Polyester fibers can be thought of as being composed of crystalline, oriented amorphous (mesophase, binding molecules) and non-crystalline (amorphous) domains. Three-phase structural models of polyester and polyamide fibers are proposed as figure below. The model includes microfibrils containing alternating amorphous and crystalline regions; these are interconnected by amorphous fibril phases formed primarily of linking molecules. Each phase is characterized by its volume fraction and orientation. [2]
Structural model of semicrystalline fibers [2]
- Fiber Structure
The fiber structure is highly dependent on the process parameters of fiber formation, such as spinning speed, drawing, and heat-setting. The final fiber structure is highly dependent on temperature, draw rate, draw ratio, relaxation and heat-setting conditions. The crystalline and amorphous orientation and the percentage of crystallinity can be adjusted significantly in response to these process parameters.
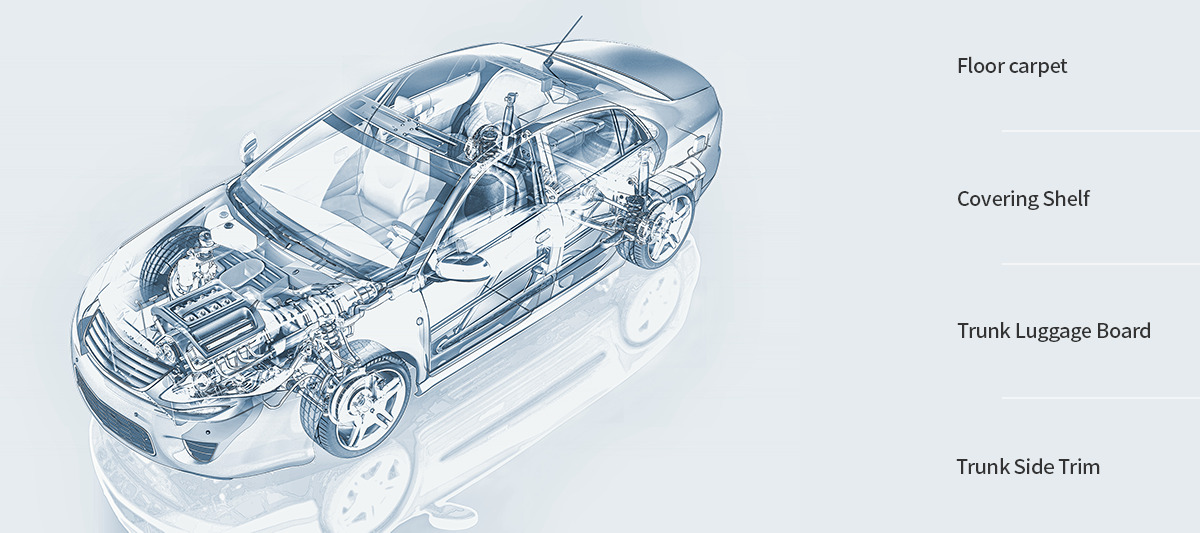
Polyester fiber is used for industrial products
Our range of industrial offerings caters to diverse applications, each featuring distinct specifications tailored to various markets including automotive, appliance, industrial manufacturing, and packaging materials. This dynamic end market, subject to constant evolution, encompasses a wide array of products such as upholstery, paneling, hood linings, trunk liners, molded trim, and more.
Utilizing fabric crafted from Recycled Polyester Staple Fiber is prevalent in nearly all automobiles across the globe, owing to its cost efficiency and durability. This choice not only contributes to cost reduction passed on to customers but also enhances the overall feel and finish of the vehicle.
Polyester fiber is used for Home Textile & Bedding
Our polyester fiber products are used in mattresses, quilts and non-woven. Our customers are bedding suppliers, mattress fabricators, which recognized names in the bedding industry.
Our range of polyester fiber products offers various lines of craft items including fiberfill, pillows, decorative pillows, pillow inserts, toys, and other materials commonly used by home craft enthusiasts. These products are suitable for use by both hand and machine quilters.
Recycled solid polyester fiber is a key material employed in filling a wide array of products, including soft toys, cushions, sofas, and various furniture pieces. Opting for recycled polyester fiber not only offers cost-efficiency but also contributes positively to the environment.







Advantages of polyester fibers:
Disadvantages of polyester fiber:
1. The first disadvantage of polyester fiber is its poor moisture absorption, which is caused by its texture.
2. The air permeability is poor.
3. The third is that its dyeing performance is poor, and it needs to be dyed with disperse dyes under high temperature.
Why people choose polyester fiber:
1. Advantages of polyester fiber Polyester fiber has high strength and elastic recovery capacity, so it is firm and durable, wrinkle resistant and iron free.
2. It has good light resistance. In addition to being inferior to acrylic fiber, its light resistance is better than that of natural fiber fabrics, especially behind the glass. It is almost on a par with acrylic fiber.
3. In addition, the polyester fabric has good resistance to various chemicals, and is not damaged by acid and alkali, and is not afraid of mold or moth.