What is PLA Fiber (Polylactic Acid Fibers)?
PLA fiber, also known as corn fiber, is made from starch based biomass such as corn and potato. PLA fiber has environmental protection, non-toxic, antibacterial, flame retardant and good biocompatibility, and can be completely biodegradable under normal composting conditions.
PLA Fiber is made from PLA (PolyLactic Acid). also, PLA is made from corn. The fiber products are highly smooth and completely non-irritating to the skin, also they are 100% biodegradable and compostable. The fiber-forming substance is a lactic acid polymer in which at least 85% by weight are lactic acid ester units derived from naturally occurring sugars (sugar beets and corn).
Although compostable, polylactic acid is quite durable in most applications. In fact, PLA does not readily degrade unless it is exposed to high humidity and elevated temperatures (≥ 60°C) which results in rapid decomposition of the fiber. Thus, for most applications, its durability is acceptable or good. The tensile strength of PLA fibers is comparable to those of polyester fibers. However, PLA has a low Tg of only 55 – 60°C and thus, is less heat resistant than polyester (PET). It is also more flammable and less abrasion-resistant.
PLA is the only melt-processable natural-based thermoplastic that can be melt spun into filaments which is often the most economic and convenient method. However, the fiber can be also spun by several other methods. Dying can be accomplished with dispersing or direct dyes using conventional processes when avoiding (strong) alkaline conditions.
PLA fiber is a type of synthetic fiber made from polylactic acid (PLA), a thermoplastic polyester derived from renewable sources such as corn, sugarcane, or cassava. PLA fiber is biodegradable and compostable, and has many applications in textiles, agriculture, and medicine. PLA fiber is also used for 3D printing, as it has low melting point, high strength, low thermal expansion, and good layer adhesion. PLA fiber is considered a more environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based polyester fibers such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
PLA, also known as polylactide, belongs to the polyester family. PLA is a polymer obtained by polymerizing lactic acid as the main raw material. The source of raw materials is sufficient and renewable, which mainly includes corn, cassava, etc. The production process of PLA is pollution-free, and the product can be biodegraded to realize the cycle in nature, so it is an ideal green polymer material.
PLA can be prepared by direct polycondensation and ring-opening polymerization, as shown in the figure below. The former production method is simple, but it is difficult to obtain high molecular weight PLA. The latter method is often used for the synthesis of high molecular weight, high stereoregularity PLA.
Production process of PLA Fiber
PLA fiber starts with an abundant, natural resource – plants (usually corn and potatoes). Starch in plants ferments to produce lactic acid. From lactic acid a molecule called lactide is created. Water is then removed and it gets crystallized to create the high-performance polymer – polylactide (PLA). Also known as polylactide, PLA is a non-aromatic polyester derived 100% from renewable resources.
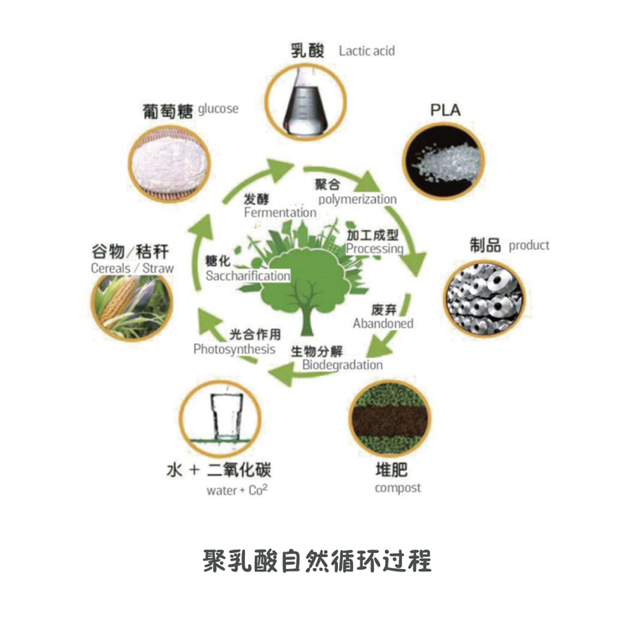
Polylactic acid fiber, referred to as PLA fiber, also known as corn starch fiber, is extracted from corn and other plants, fermented to produce lactic acid, and then refined and polymerized to form polylactic acid, and then processed into clothing products through spinning and weaving . After being discarded, it can be decomposed into carbon dioxide and water through the action of microorganisms, and can be absorbed and utilized by plants again through photosynthesis. Such a circular process truly embodies the concept of sustainable development of green environmental protection and circular economy.
Properties of PLA Fiber
- PLA fiber are 100% bio-based synthetic thermoplastic fibers, which are favored because of their wide source of biomass raw materials, green production process, degradability, and excellent comprehensive performance.
- PLA fibers are considered the most promising sustainable and biodegradable fibers to replace conventional polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polyester fibers in textile products.
- PLA fibers have good biodegradability and can be completely decomposed into CO2 and H2O in nature after being discarded. Through photosynthesis, the two can be turned into starch, the raw material of lactic acid.
- PLA fibers have the physical and mechanical properties of high crystallinity, high orientation, high heat resistance and high strength. The physical properties of PLA fibers are similar to those of PET fibers and nylon fibers. The performance comparison of the three is shown in the table below.
| Project | PLA | PET | Nylon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical properties | Specific gravity | 1.27 | 1.38 | 1.14 |
| Refractive index | 1.4 | 1.58 | 1.57 | |
| Melting point °C | 170 | 255 | 220 | |
| Tg °C | 57 | 70 | 40 | |
| Moisture absorption rate | 0.6 | 0.4 | 4.5 | |
| Mechanical properties | Strength g/d | 3.5-5.0 | 4.5-5.5 | 4.5-6.0 |
| Elongation % | 40 | 30 | 60 | |
| Dyeability | Dye | Disperse | Disperse | Disperse |
| Temperature °C | 100 | 130 | 100 | |
- PLA fibers are biocompatible and can be safely implanted into the body without toxic side effects.
- PLA fiber has a high oxygen limiting index (LOI 24-29), good self-extinguishing after combustion, low combustion smoke, and good flame retardancy.
Application And Research
PLA fibers are mainly used in clothing, medical, interior decoration and food packaging and other fields, and they have good dyeability and biocompatibility. Notably, since the degradation product lactic acid is metabolically harmless, PLA fibers have attracted much attention as biomedical materials, such as implants and sutures. Furthermore, PLA fibers have been found to be one of the most favorable matrix materials in the field of tissue engineering. Marco Santoro et al. reviewed recent advances in PLA nanofiber scaffolds for musculoskeletal, neural, cardiovascular, and skin tissue engineering. [2]
PLA fiber is biodegradable, the fiber is soft and smooth, and the strength is moderate. The products made have silky luster and comfortable skin touch and feel, good hygroscopicity and quick-drying effect, good drapability, and good heat resistance. Non-toxic, natural antibacterial and anti-ultraviolet functions, it combines the effects of scratching and gloss, and has excellent wearing
Pure natural material, completely biodegradable
The raw materials for producing PLA are abundant. All natural biomass raw materials containing starch, cellulose and hemicellulose can be used to produce lactic acid, and then polymerized to produce polylactic acid. In order to avoid ” competing with people for food and land with food ” , non-food crops ( such as cassava ) can also be used as raw materials, or even organic waste (corn cobs or roots, stems, leaves, skins, straw, straw, Urban organic waste, industrial waste, etc.) can be used as raw materials to produce lactic acid, and then produce polylactic acid. These raw materials can be obtained through continuous planting. As no oil or wood is used, this will protect limited oil and wood resources. Compared with natural fiber cotton, the yield per mu of PLA fiber is large. For example, the yield per mu of cotton is only 63Kg, while that of corn can reach 325Kg. Therefore, the same acre of land can produce more PLA fiber than cotton fiber. In addition to this, 29,000 tons of water are required to produce one ton of cotton fiber, while less than 100 tons of water are required to produce one ton of PLA fiber.
The melting point of PLA fiber is lower than that of polypropylene fiber, and the energy consumed to produce PLA fiber is less than that of the three major synthetic fibers, and also lower than that of PTT and Lyocell fibers. The comprehensive energy consumption of the product is currently the lowest in the production of major chemical fibers.
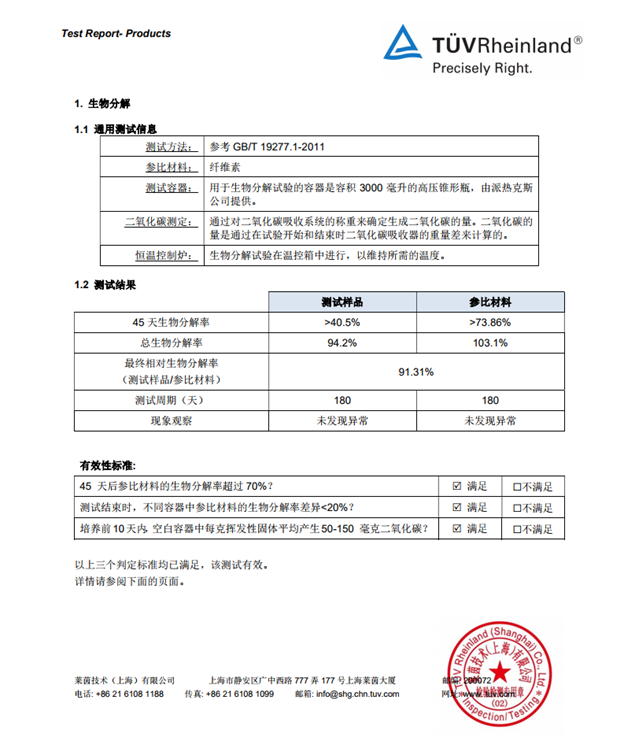
PLA fiber can be degraded naturally in nature, and can be quickly decomposed into carbon dioxide and water under the action of microorganisms in soil or seawater. According to the test of relevant departments, more than 40.5% of PLA fiber can be degraded after 45 days of landfill, and 94.2% after 180 days . It can be degraded and is an environmentally friendly fiber. When PLA fiber burns, it will not emit poisonous gas, will not cause pollution, and realizes carbon cycle. It is a sustainable ecological fiber.
Lightweight, warm, skin-friendly and breathable
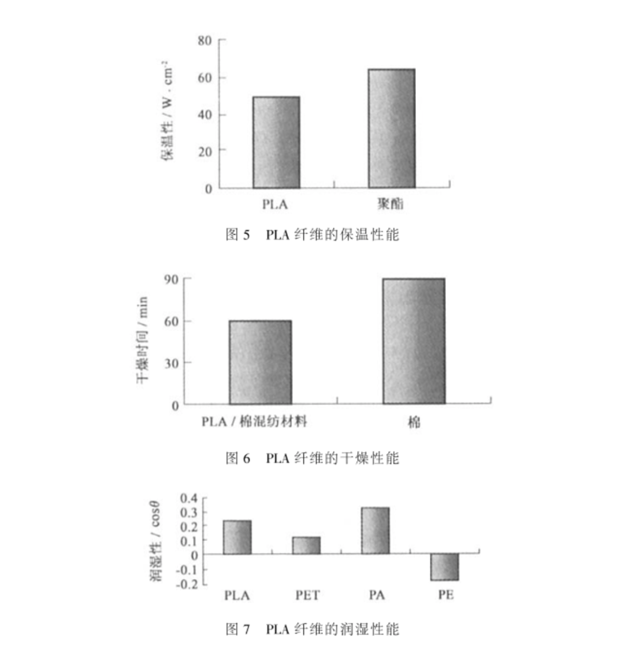
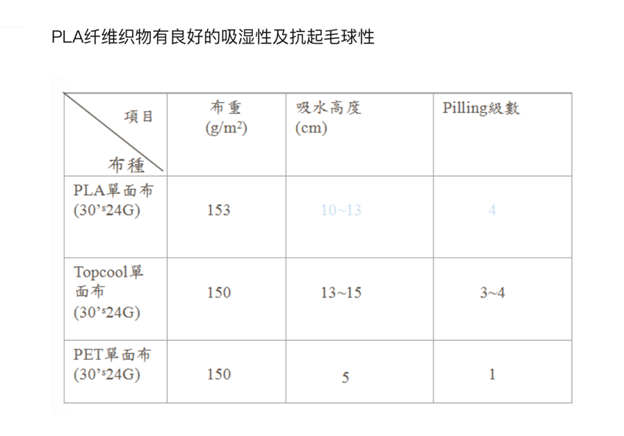
The density of PLA fiber is 1.27g/cm3, which is a lightweight fiber and tries quickly after being wetted with water without feeling sticky or heavy, The young’s modulus of PLA fiber is between polyester and nylon, so it feels slightly harder than nylon, but much softer than polyester. PLA fiber has a low refractive index and has elegant luster like silk. When worn in winter, the thermal insulation of PLA fibers is more than 20% higher than that of cotton and polyester fibers. In summer, PLA fiber fabrics have excellent moisture permeability and water diffusivity, absorb sweat and dry quickly, and can quickly take away body heat through evaporation. There is a refreshing feeling all year round.
The surface of PLA fiber is weekly acidic, and its PH value is 6.0-6.5, which is weekly acidic, and the skin of a healthy human body is also weekly acidic, so PLA fiber has good compatibility with weakly acidic skin. at the same time, when a person is exercising, the sugar in the body turns into energy, and lactic acid is formed in the body (muscle). The fact that the body itself accepts lactic acid is a safe material. It has natural anti-allergic and skin-friendly functions on human skin, and is especially suitable for making various skin-friendly products.
Good resilience, wrinkle resistance and shape retention
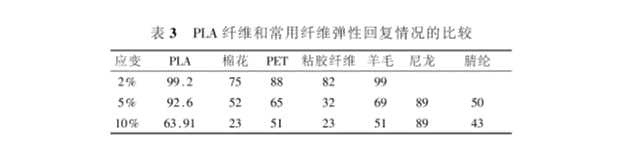
The initial modulus of PLA fiber is low, the drapability is small, and the fabric has good drapability. When the tensile deformation of PLA fiber is 5%, the elastic recovery rate is as high as 93%, which shows that PLA fiber has good bulkiness and elastic recovery rate, which is better than nylon. The fabric made has good elasticity and good wrinkle resistance, which is very suitable for making sportswear.
In addition, PLA fibers and their fabrics do not absorb ultraviolet rays, and their strength and elongation are not greatly affected by long-term ultraviolet radiation. After 500 hours of outdoor exposure, PLA fiber can still retain about 55% of its strength.
Natural antibacterial, antibacterial, anti-mildew
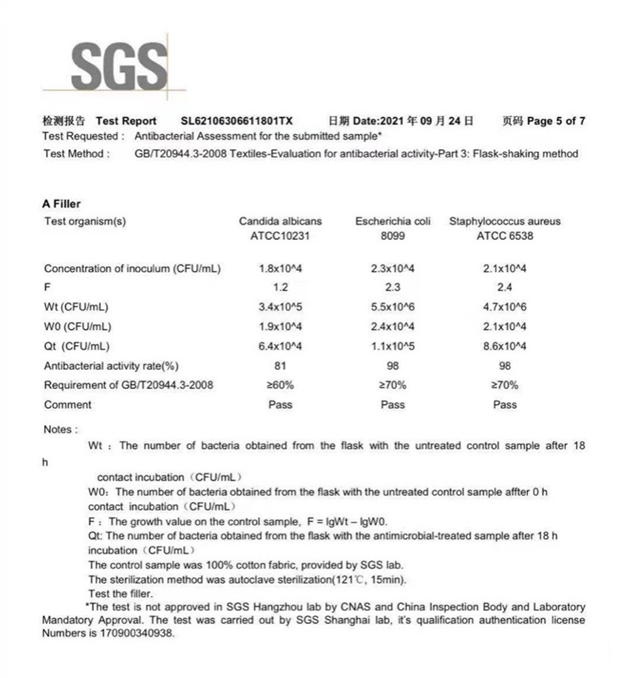
PLA fiber has natural antibacterial and antibacterial ability, without adding any other ingredients, it can form a natural and stable antibacterial environment on the surface of the fiber, making it difficult for Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans to reproduce.
Good flame retardancy
The limiting oxygen index of PLA fiber reaches 24-29, which is the highest among commonly used fibers, and is already close to the national standard’s requirement for the limiting oxygen index of flame-retardant fibers to be 28-30. PLA fibers are not easy to burn, and have good self-extinguishing properties after burning. During the burning process, only slight smoke is released, and the amount of smoke is very small.
Easy to dye, good coloring, bright color
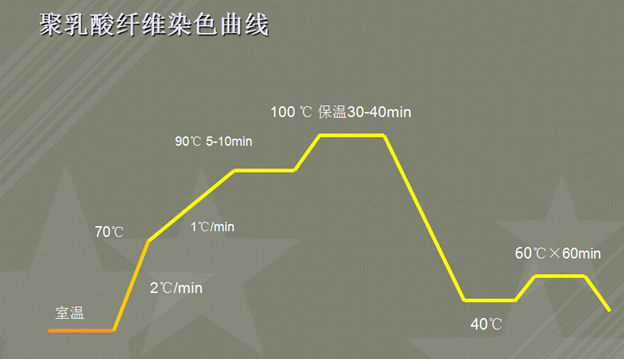
PLA fiber is dyed with disperse dyes like polyester fiber, but it is easier to dye than polyester fiber. The pre-dyeing treatment, dyeing, post-dyeing and finishing of knitted/woven and interwoven/blended fabrics must follow the principles of low temperature, low alkali and short process. Generally, it can be dyed at 95°C to 100°C. For a small number of cases that need to be dyed dark, it can be dyed at 110°C. Even so, the dyeing temperature is lower than that of polyester. The dyeing temperature of PLA fiber is low, the setting temperature is low, and strong alkali is not used, which is in line with the trend of energy saving and emission reduction.
Due to its lower refractive index, the color of PLA fiber dyed is also brighter.
Advantage of PLA Fabric
- 100% From Plants Antibacterial Naturally
- Low Carbon UV-stable
- 100% Biodegradable & Compostable
- Renewable & Sustainable
- Antibacterial Naturally
- UV-stable
Read more: https://vnpolyfiber.com/what-is-pla-what-is-polylactic-acid/