What is organic cotton?
Organic cotton is an eco-friendly version of ordinary cotton. If cotton has to be sold as organic cotton, it has to meet strict standards. With increasing number of consumers, conscious of protecting nature and supporting sustainable production, the importance of organic cotton is increasing day by day and the reasons why it is considered better is very obvious.

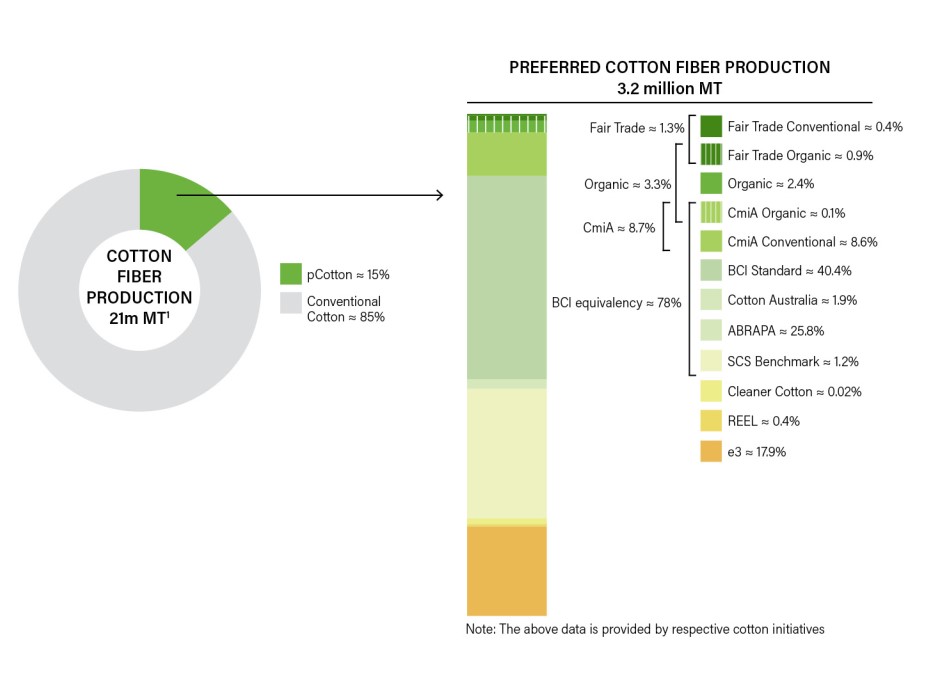
The cotton fiber market was estimated at 21.07 million MT in 2016 (ICAC). The preferred cotton segment which is made up of Organic, Fair Trade, CmiA, BCI, REEL, Cleaner Cotton, and e3 makes up approximately 15 percent (3.2 million MT) of total cotton fiber production (excluding recycled cotton). This is a significant increase from nine percent of the cotton market share in 2015.
The two factors that contributed to this shift were: firstly the reduction in the overall cotton fiber production, from 26 million MT in 2015 to 21 million MT in 2016; and secondly preferred cotton fiber production increased from 2.2 to 3.2 million MT between 2015 and 2016.
ORGANIC COTTON PRODUCTION IN 2015 and 2016
Total: 18 countries / Top 7 Countries = 97%
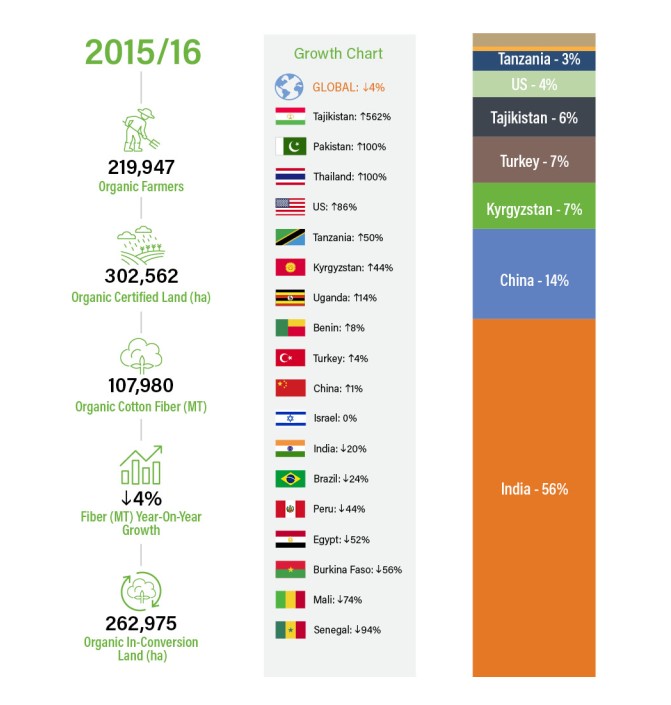
In 2015/16, total organic cotton fiber production amounted to 107,980 mt. There were 18 organic cotton-producing countries in 2015/16. While the number of producing countries remains the same as 2014/15, Colombia, Ethiopia, and Madagascar were replaced by Thailand and Pakistan.
The top seven countries – India, China, Kyrgyzstan, Turkey, Tajikistan, the US, and Tanzania – account for 97 percent of total production.
Overall, production decreased by 4 percent. The primary reduction came from India, the fall was offset by an increase in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan.
How is the organic cotton grown and cultivated?
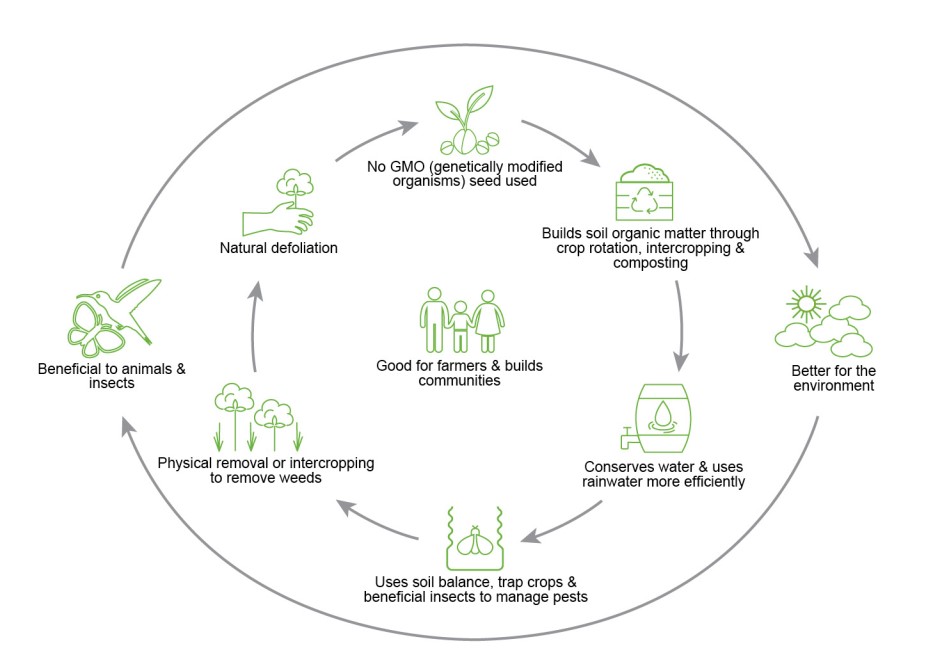
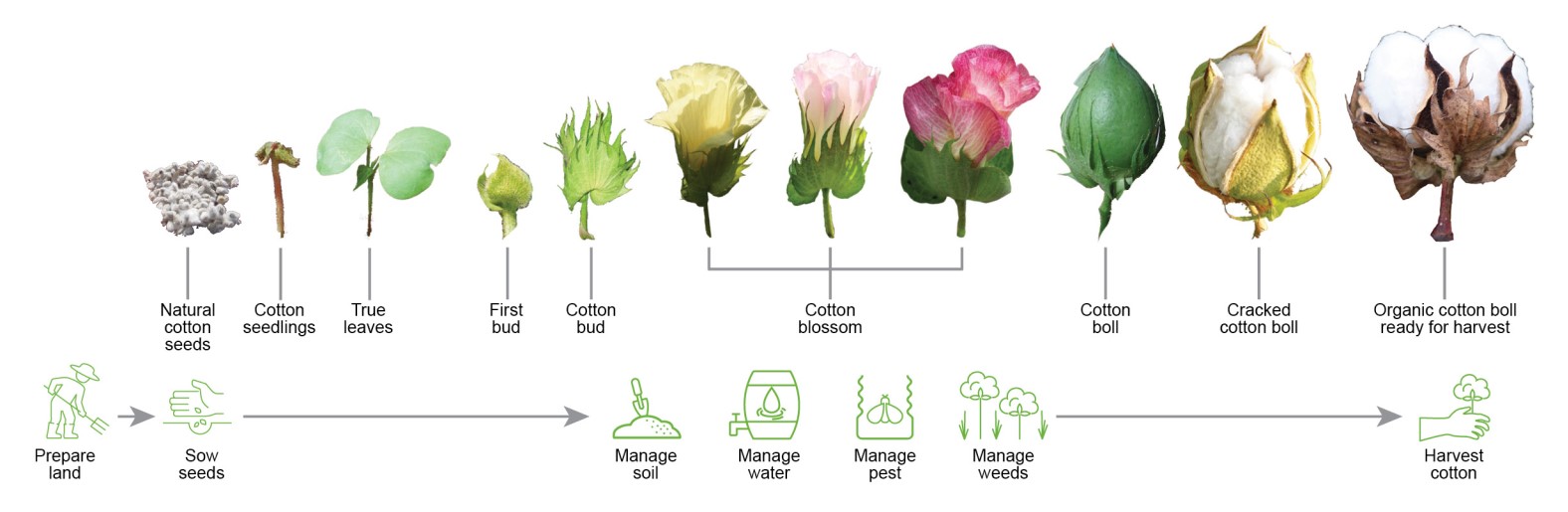
The journey of organic cotton starts with securing untreated, natural (non-GMO) seeds. These seeds are often hard to come by and this can be a real issue for farmers. Once the seed is secured, the land needs to be prepared and the seed was sown. It takes approximately 60 to 70 days from planting until the first flower appears, and boils appear 50 to 70 days after bloom. The growth cycle of the cotton plant lasts for approximately 5-6 months. During this time, soil fertility, water, pests, and weeds need to be managed. 45 days after boils appear, the cotton boil will begin to naturally split open along the boils’ segments. Once the cotton boil is fully dried and fluffed, it is ready for harvesting.
Only natural, untreated non-GMO (genetically modified organism) seeds are picked for cultivation. In many countries such as the US, federal regulations prohibit the use of genetically engineered seeds for organic cotton farming. The health of the soil in the growth terrain will be maintained through a series of steps such as crop rotation; only organic matter is used as fertilizers.
To ensure weed control, beneficial insects and trap crops are used instead of aerial spraying of insecticides or pesticides. This helps maintain and preserve the natural balance of the soil and keeps the farmland healthy.
When it comes to harvesting, natural defoliation is preferred over artificial or induced defoliation with toxic chemicals. To facilitate organic and natural harvesting, freezing temperatures and/ or use of proper water management is practiced. To project the crops, warp fibers are stabilized by double-plying or nontoxic cornstarch.
When it comes to whitening of the fibers, organic cotton steers clear from chlorine bleaching which is what makes your regular cotton white, and uses safe peroxides instead.
To finish off, it is soft scoured in warm water with soda ash, for a pH of 7.5 to 8. Finally, when it is taken for dyeing, low-impact fiber-reactive or natural dyes with low metal and sulfur content are used.
All things considered, organic cotton is the safer, more sustainable future of clothing.
Are you up for the 2025 Sustainable Cotton Challenge in which many brands and retailers are ready to committed to source 100% of their cotton from the most sustainable sources by the year 2025. As consumers, we have a right to be in charge of the future, too.
Why is organic cotton considered best for babies?
Organic cotton is free from harmful chemicals that could irritate a baby’s delicate skin or cause allergic reactions. Organic cotton is typically softer and more breathable than conventional cotton and would not cause painful rashes on the soft baby skin. It is super absorbent, breathable and comfortable. I think these points would quite frankly explain why organic cotton is used to make cloth diapers for babies. It allows air to flow freely around your baby’s sensitive skin and reduces rashes formed from chaffing. You can safely buy and use organic cotton fabric for baby clothes.
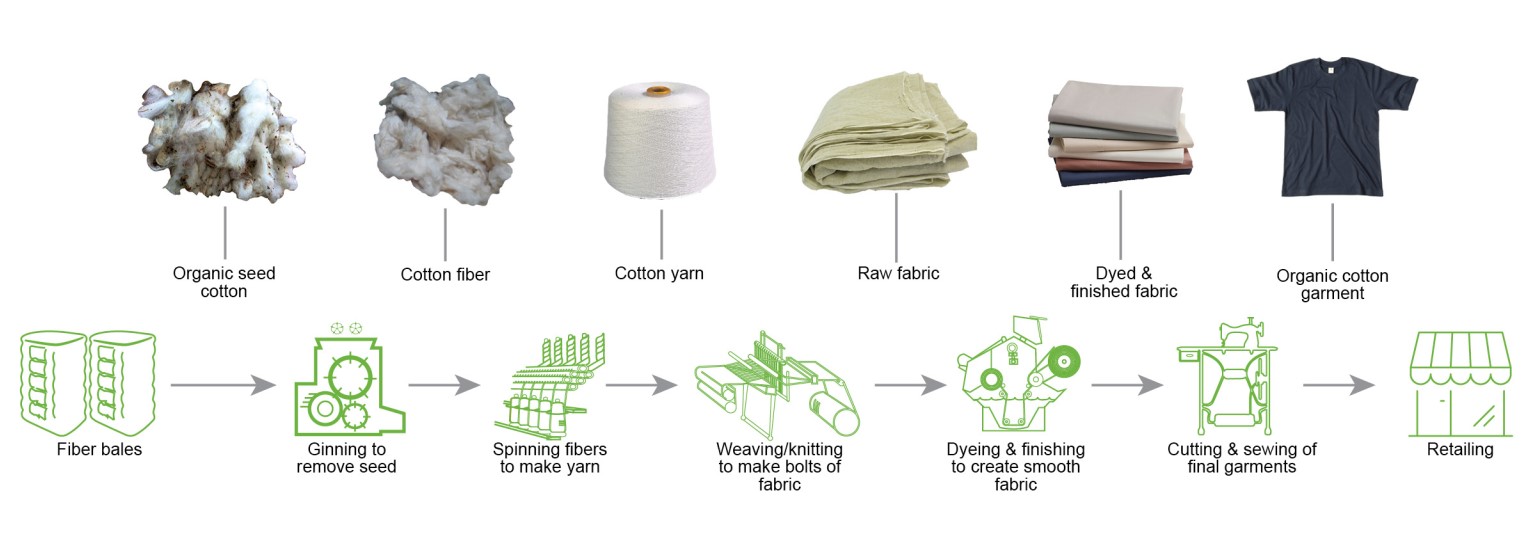
ORGANIC COTTON SUPPLY CHAIN
The general process of transforming seed cotton from the farm into the final garment includes ginning, spinning, weaving/knitting, dyeing, finishing, cutting, and sewing. Organic certification ensures that the cotton passing through each stage of the manufacturing process is tracked.
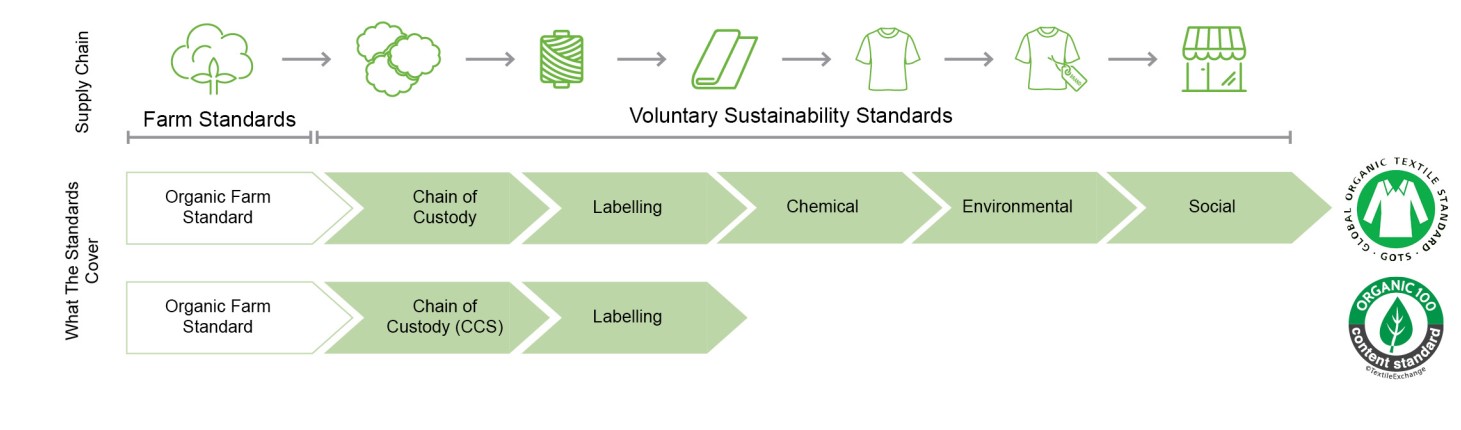
ORGANIC COTTON STANDARDS
Organic cotton certification is carried out at two levels:
- Produced according to the IFOAM Principles of Organic Agriculture and certified to the IFOAM Family of standards at the farm level, and
- Certified to either the Organic Content Standard (OCS) or the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) from fiber to product. OCS provides third-party assurance that the organic content in your clothes can be traced back to the source, while GOTS traces the organic content in your clothes and ensures that it is processed socially and sustainably.
Cotton vs Organic cotton
Around 30 million tons of cotton is produced every year. Cotton remains one of the most pesticides sprayed crops in the world despite its unmatched popularity. According to reports that emerge, cotton farming accounts for 25% of the world’s insecticides and about 10% of the pesticides.
A huge amount of herbicides (chemicals for weed removal) and defoliants (herbicidal chemicals sprayed or dusted on plants to cause their leaves to fall off) are often always used in the process of cultivation and extraction of cotton fibers.
Growing one pound of unbleached cotton needs a third of its portion as chemical fertilizers. 150 pounds of synthetic fertilizer gets used up for every acre, averaging up to 2 billion pounds of nitrogen-based fertilizer per crop. Many of them have proved to be Carcinogenic.
Now imagine small kids wearing clothes created with these heavily treated, processed, and sprayed cotton? It is not a pleasant thought.
With organic cotton, you do not need to fear how it is made. It is made under controlled farming practices using the least amount of fertilizers and following all the norms and regulations that organic farming calls for.
Organic cotton costs more than conventional cotton. The cotton farmers have to maintain their livelihood. The cost of organic cotton will have to cover the extra in organic value addition.
Organic Cotton is the best eco-friendly fibers
Like all organic products, organic cotton was harvested without the use of GMOs, pesticides, insecticides, or other chemicals that could harm the environment. Global expertise is already well developed to gin, spin, and knit cotton.
Organic cotton plays a complementary role with other eco-friendly fibers with which it is often blended.
The fabric has the same quality as conventional cotton but does not a negative impact on the environment. Organic cotton addresses most of the environmental challenges which conventional cotton production faces. Only 0.7% of global cotton production is organic.
It is grown from non-GMO seeds and without the use of pesticides, insecticides, or fertilizer. Unlike conventional cotton, organic farmers use ancestral farming methods, including crop rotation, mixed farming, or no-till farming to preserve the soil. Organic cotton uses up to 71% less water than conventional cotton according to some sources.
Organic cotton farmers are not exposed to harmful substances.
Several organizations have established certifications for organic cotton such as GOTS, USDA-NOP, Organic Content Standards, IVN, and Naturland. Certification is the only proof that a product is truly organic.
Organic cotton is grown in the USA. It can be locally grown and transformed.
Pros of organic cotton:
- No transformation. Just ginning (removing the seeds from the fibers)
- Affordable price.
- Well-developed expertise.
- Biodegradable.
- Locally grown.
Cons of organic cotton:
- Can need irrigation water.
- Very demanding on the soil.
- Must be certified.
- Susceptible to pests and diseases (hence the extensive use of chemicals to grow non-organic cotton). There is always a risk of losing the crop or getting a lower yield.
Benefits of Organic cotton fabric
Switching to organic cotton could consciously be the best decision you make because of the following reasons:
- Sustainable and Pro-nature : As I previously discussed in this article, organic cotton is so much more environmental-friendly. It is ethically produced, more sustainable, and overall chemical-free. Compared to normal in-organically made cotton, the manufacturing processes of organic cotton are a lot more rigid and follow strict standards. This not only minimizes the negative impact on the environment but ensures high customer value.
- The organic cotton fiber is grown using methods and materials that have a low impact on the environment. Unlike in the cultivation of ordinary cotton, toxic and persistent disease-causing pesticides, (like Endosulphan) and synthetic fertilizers are avoided altogether. This organic production allows for replenishing and maintaining soil fertility.
- Better for your health and skin : The primary difference between non-organic and organic cotton is that the latter is remarkably softer and a lot better on the skin.
- Plus, its lack of chemical treatments makes for the best alternative if you have skin allergies or other ailments.
- In addition, it is non-irritable, breathable, and suits sensitive skin.
- Better environmental outcomes for the future: Organic cotton farming with its better farming practices such as crop rotation, better water usage, and soil preservation, safe and natural pest removal, organic fertilizer usage is your best bet if you want the preservation and restoration of the natural environment.
Key reports and tools:
Thirsty for Fashion, Soil Association (2019)
Is Cotton Conquering It’s Chemical Addiction? Pesticide Action Network (2017, revised 2018)
Three Free Tools To Help You Source Organic Cotton from Cotton2040 and Textile Exchange
Reference: Organic Cotton fabric details; Another good article on the goodness of organic cotton; ota.com ; Read more about 2025 Sustainable Cotton Challenge here ; Non profit organisations working for organic cotton like Cotton connect, Fairtrade international, Pesticide Action network, Soil association, BioRe foundation.
https://respecterre.com/blogs/news/the-best-eco-friendly-fibres