What is viscose?
Viscose fiber comprises two categories: viscose filament fiber and viscose staple fiber. Viscose fibers are classified as cellulose fibers derived from natural materials such as cotton and other plant-based sources. Regenerated cellulose fiber, known as viscose fiber, utilizes natural cellulose as its primary raw material. The manufacturing process involves the production of soluble cellulose xanthate through a series of steps including alkalization, aging, and xanthation. Following this, the soluble cellulose xanthate is dissolved in a dilute alkaline solution, leading to the formation of viscose rayon. The final stage involves the wet spinning process to produce viscose fiber. Variants of viscose fiber, such as ordinary viscose fiber, high wet modulus viscose fiber, and high tenacity viscose fiber, are differentiated based on the specific raw materials used and the associated spinning techniques employed in their production.
Characteristics of Viscose
Natural & Comfortable: Viscose-rayon is composed of 100% wood cellulose, serving as a natural substitute for synthetic fabrics such as acrylic, polyester, and nylon, which are derived from petroleum. The inherent absorbent properties of cellulose fibers facilitate effective dye uptake, resulting in vibrant, luminous colors while maintaining the material’s natural sheen.
Characterized by a soft, breathable texture akin to cotton and a smooth finish comparable to silk, viscose-rayon exhibits excellent draping qualities, enhancing comfort and user satisfaction.
Viscose rayon provides numerous advantages in various applications, including apparel, home textiles, and personal hygiene products. Composed of wood cellulose, viscose rayon exhibits a lustrous appearance and a tactile quality akin to cotton, while offering comparable characteristics in terms of comfort, breathability, and absorbency. Its ease of dyeing enables its utilization in the manufacture of garments such as underwear, infant clothing, skirts, shirts, and dresses that are gentle against the skin. In domestic settings, it serves as an optimal textile for premium bed linens, towels, tablecloths, napkins, upholstery, curtains, and drapes.
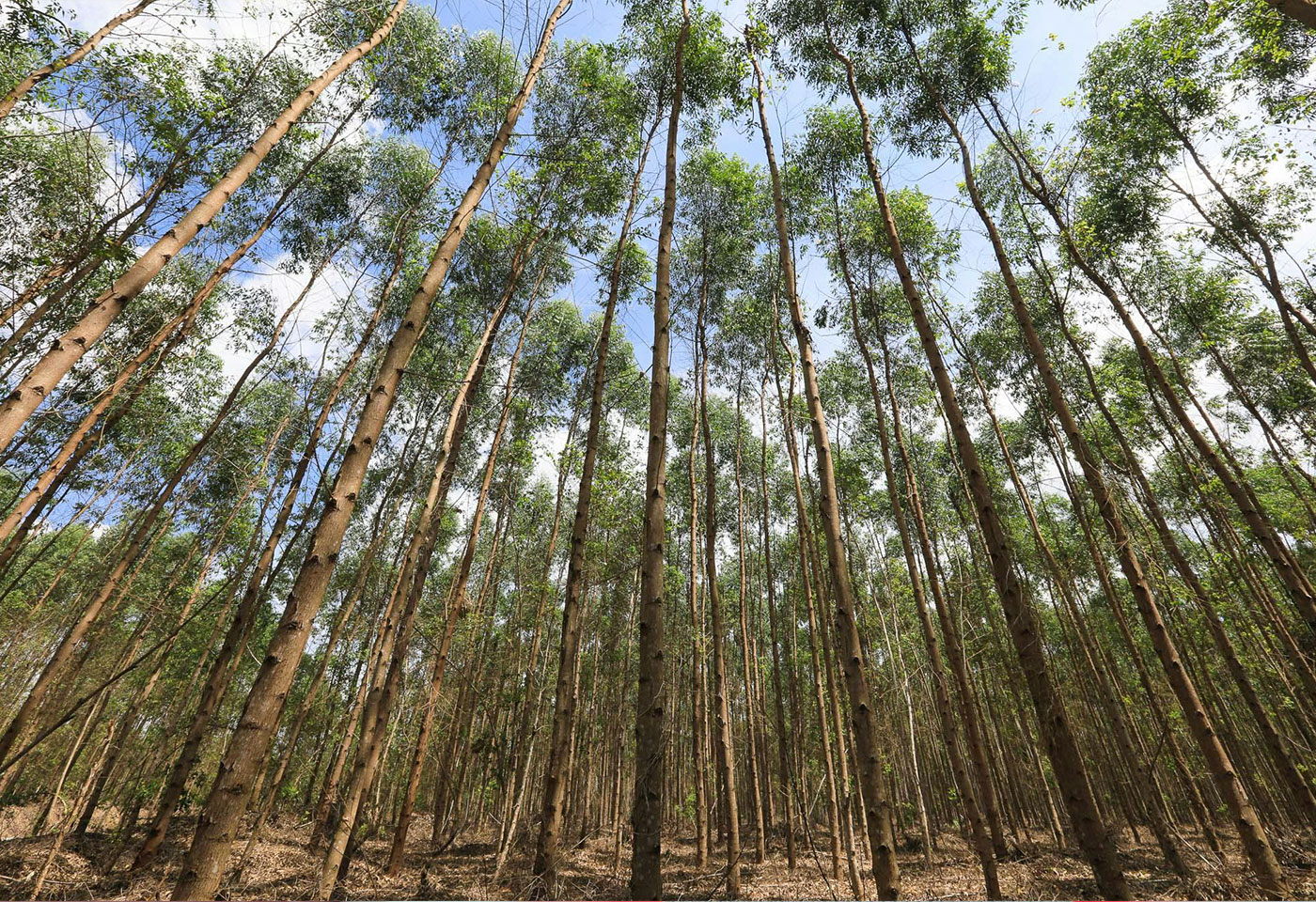
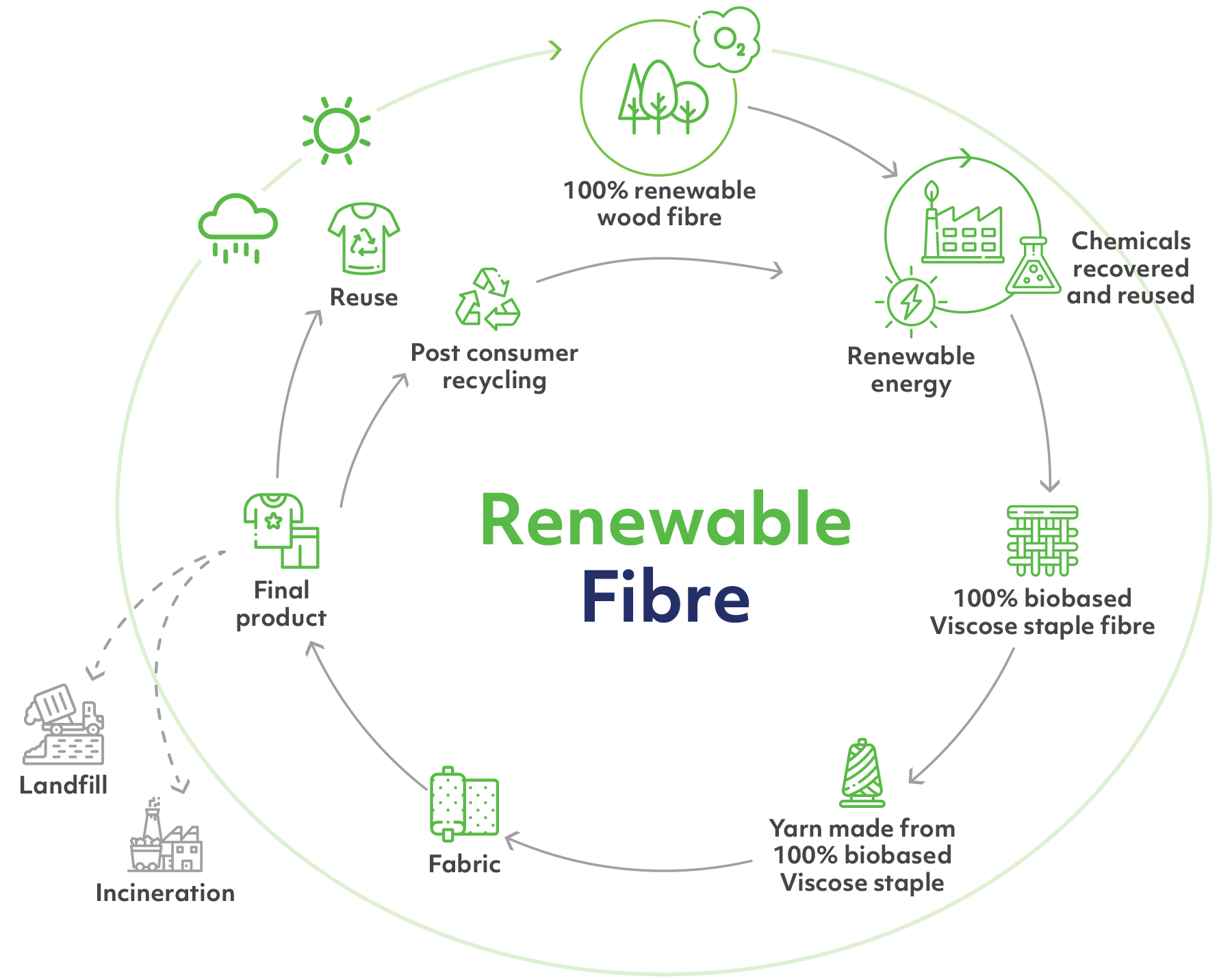
Renewable & Biodegrable: The source of our wood fiber is sustainably managed plantations and forests. These trees, classified as renewable resources, undergo harvesting cycles approximately every five years, thereby ensuring a consistent supply of renewable raw materials.
Viscose-rayon is comprised of natural plant-based polymers, rendering it biodegradable and capable of naturally decomposing in soil environments.
Viscose rayon is a fully biodegradable substitute for synthetic fabrics such as acrylic, polyester, and nylon, which are derived from petroleum. The cellulose pulp sourced from sustainably managed fast-growing plantations of acacia and eucalyptus trees also positions viscose rayon as a favorable alternative to cotton, which is cultivated on arable land using significant volumes of water. The demand for viscose rayon is on the rise as consumers increasingly seek high-quality materials against their skin.
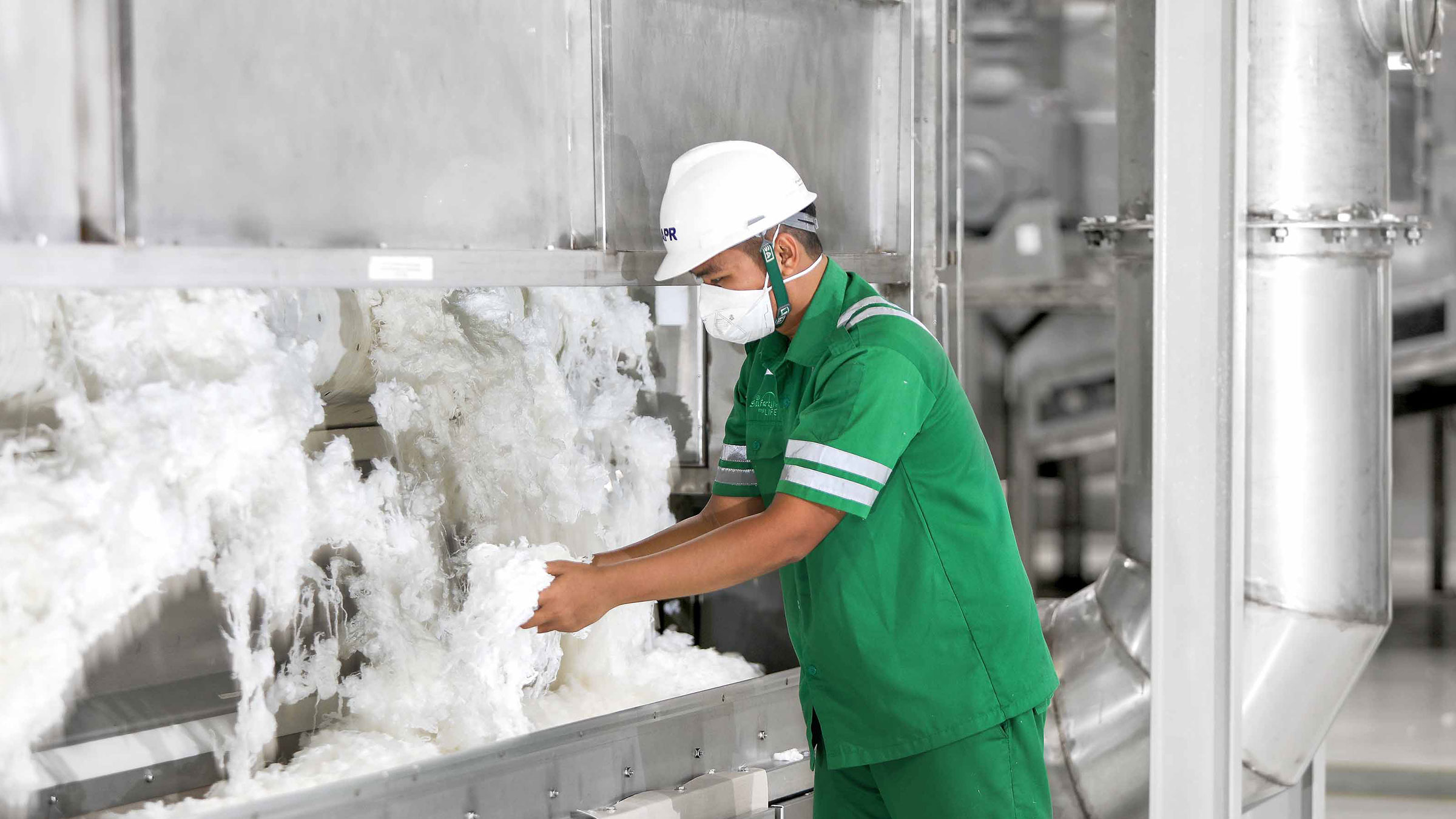
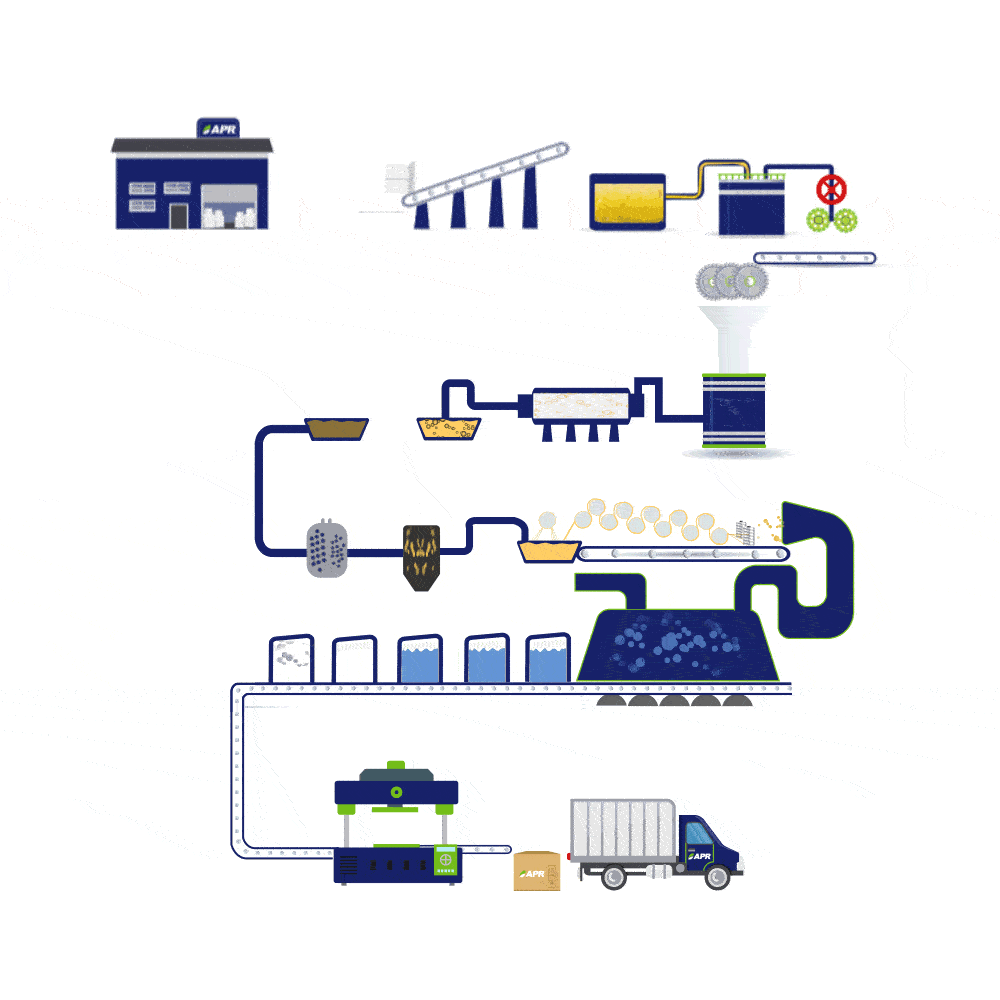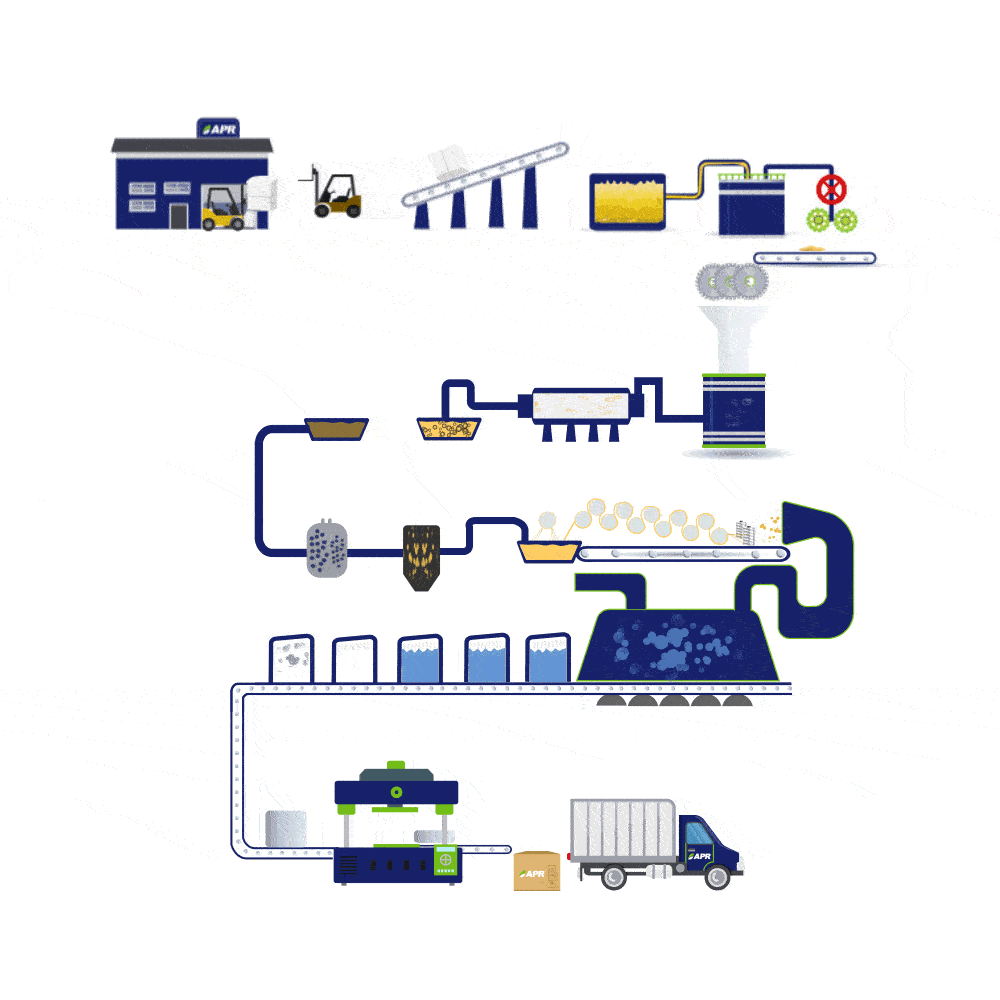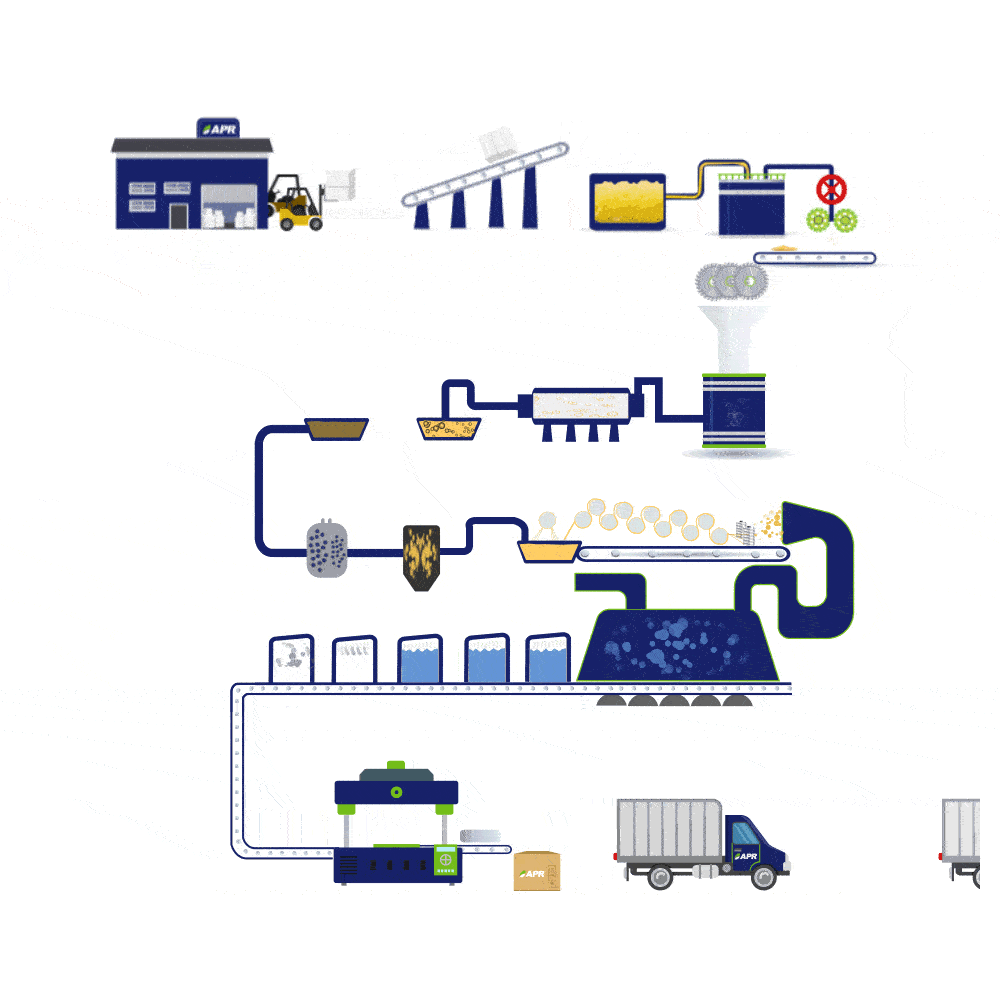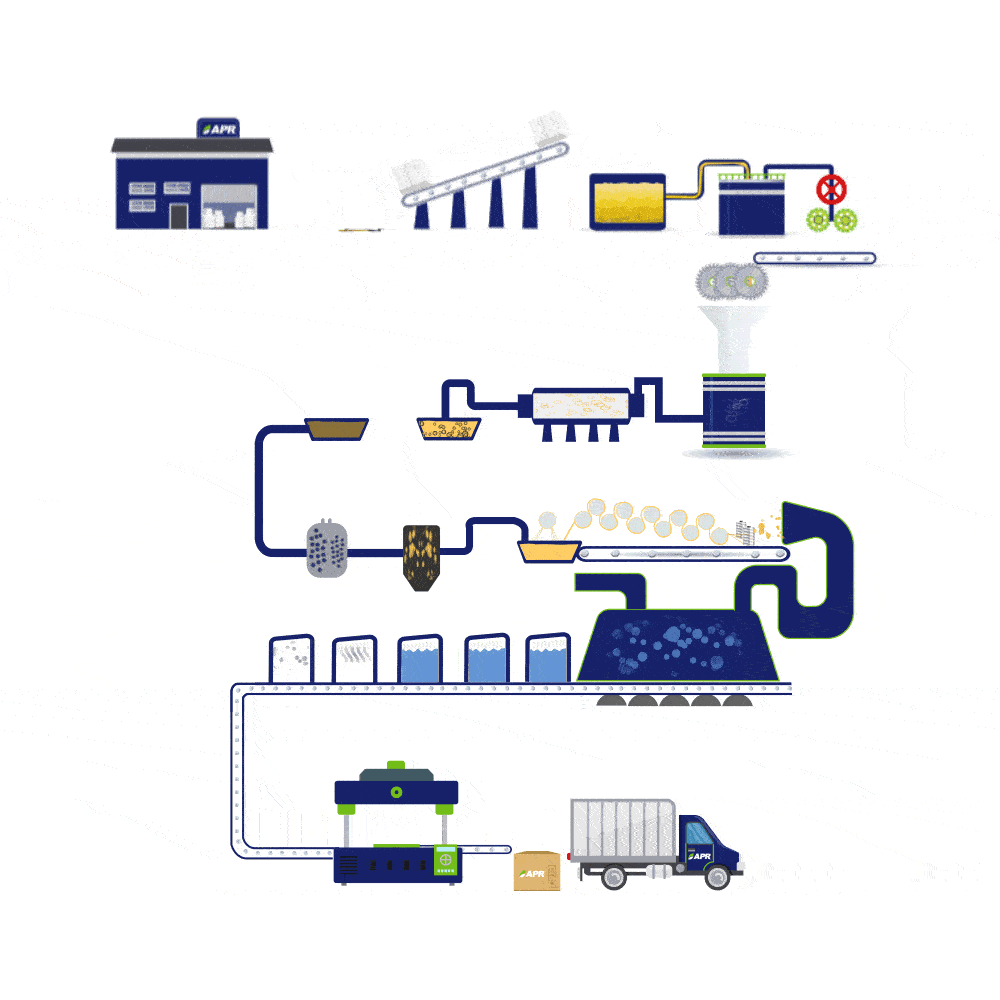
Viscose-Rayon Production Process
Step 1: Steeping – Dissolving Wood Pulp is submerged in Sodium hydroxide or Caustic soda (NaOH) in order to swell the cellulose fibres and convert cellulose into alkali cellulose.
Step 2: Pressing – The swollen alkali cellulose is compressed to a wet weight equivalent of 2.5 to 3.0 times the original pulp weight to obtain an accurate ratio of alkali to cellulose.
Step 3: Shredding – Alkali cellulose is produced by shredding the material. An increased surface area is formed thereby increasing the ability of the alkali cellulose to react in the steps that follow.
Step 4: Ageing – The alkali cellulose is aged under controlled conditions to depolymerise the cellulose for better product quality and production efficiency.
Step 5: Xanthation – In this step, the aged alkali cellulose crumbs are placed in vats and allowed to react with carbon disulphide (CS2) under controlled temperature to form cellulose xanthate.
Step 6: Dissolving – The yellow crumbs of cellulose xanthate are dissolved in a caustic solution.
Step 7: Ripening – The viscose is allowed to stand for a period to “ripen”, which results in a honey-like solution.
Step 8: Filtering – The viscose is filtered to remove undissolved particles that might disrupt the spinning process or cause defects in the rayon filament.
Step 9: Degassing – Trapped air in the viscose is removed, or they would cause voids, or weak spots, in the fine rayon filaments.
Step 10: Spinning – Viscose passes through the spinnerets and is immersed in a spin bath to produce rayon filaments.
Step 11: Drawing – The rayon filaments are stretched while the cellulose chains are still relatively movable.
Step 12: Washing – The freshly regenerated Rayon is washed to remove salts and other water-soluble impurities.
Step 13: Cutting – The fibre is cut into various lengths by passing the fibre through a rotary cutter.
Step 14: Drying – The wet viscose staple fibres are dried to an ideal moisture content of 9-14%.
Step 15: Baling Press – Our viscose staple fibre is packed and is ready for shipping.
 Viscose Fiber Market
Viscose Fiber MarketDue to the COVID-19 pandemic, the global Viscose Fiber market size is estimated to be valued at USD 15,490 million in 2022 and is projected to reach an adjusted size of USD 20,520 million by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% during the review period. Taking into account the economic changes resulting from this health crisis, Viscose Filament Yarn, which accounted for a certain percentage of the global Viscose Fiber market in 2021, is anticipated to achieve a projected value of USD million by 2032, experiencing a revised percentage CAGR in the post-COVID-19 phase. Meanwhile, the Spinning Clothing segment is forecasted to undergo a percentage CAGR throughout this period.
Key players in the global Viscose Fiber market include Lenzing, Aditya Birla Group, Sanyou, Sateri Chemical Fibre, Aoyang Technology, among others. The top five manufacturers collectively hold approximately 60% of the market share.
China constitutes the largest market segment, possessing a share of around 60%, followed by Europe, India, and Southeast Asia, each accounting for approximately 10% of the market. In terms of product categories, Viscose Staple Fiber is the predominant segment, comprising approximately 90% of the market. Regarding applications, the leading segment is Spinning Clothing, followed by Home Textile, Industry Textile, Medical Textile, and others.
1. Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
- Rising Demand for Eco-Friendly Textiles: There’s a growing demand for sustainable and biodegradable fibers, which is driving the growth of viscose fibers due to their natural origin (from wood pulp) and biodegradability.
- Development of Eco-Friendly Viscose: Manufacturers are investing in more sustainable production methods to reduce the environmental impact, such as closed-loop processes that minimize water and chemical usage.
2. Regional Shifts in Production
- Dominance of Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, India, and Indonesia, remains the largest producer and consumer of viscose fibers due to the availability of raw materials, low production costs, and increasing demand in the textile industry.
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Countries in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America are emerging as new centers for viscose production due to favorable trade policies and growing textile industries.
3. Technological Advancements
- Innovations in Fiber Quality: There is ongoing R&D focused on enhancing the properties of viscose fibers, such as improving their strength, softness, and moisture-wicking capabilities, to compete with other fibers like cotton and polyester.
- Automation and Smart Manufacturing: The viscose fiber industry is adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, including automation and digitalization, to increase efficiency and reduce costs.
4. Market Diversification
- Growth in Non-Woven Applications: While the textile industry remains the primary consumer of viscose fibers, there’s growing use in non-woven applications such as wipes, medical textiles, and hygiene products.
- Blending with Other Fibers: Viscose is increasingly being blended with other fibers (e.g., cotton, polyester) to enhance product characteristics and cater to diverse end-use applications.
5. Regulatory and Environmental Challenges
- Stringent Environmental Regulations: The viscose industry faces stringent environmental regulations, especially in Europe and North America, related to the production process, which is driving the need for cleaner technologies.
- Pressure from NGOs and Consumers: There is increasing pressure from NGOs and consumers for the industry to adopt more transparent and environmentally responsible practices, pushing companies to certify their products through eco-labels and sustainability programs.
6. Price Volatility and Supply Chain Issues
- Fluctuating Raw Material Costs: The price of wood pulp, the primary raw material for viscose fiber, is subject to fluctuations due to changes in forestry practices, demand from other industries, and geopolitical factors.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, have impacted the availability and cost of viscose fibers, prompting manufacturers to seek more resilient supply chain strategies.
7. Increasing Use in Fashion and Apparel
- Preference for Comfort and Aesthetic Appeal: Viscose fibers are favored in the fashion industry for their silk-like feel, drape, and ability to hold vibrant colors, which is boosting their demand in apparel.
- Fast Fashion Impact: The fast fashion industry, which requires low-cost, versatile fabrics, continues to drive demand for viscose fibers, though it also raises concerns about sustainability and environmental impact.
What are the factors contributing to the growth of the Viscose Fiber Market?
The escalating global demand for the following applications has significantly influenced the expansion of the Viscose Fiber market:
- Spinning Clothing
- Home Textiles
- Medical Textiles
- Industrial Textiles
What are the types of Viscose Fiber available in the market?
The market is segmented by product types, which include the following categories that are projected to capture the largest market share of Viscose Fiber in 2024:
- Viscose Filament Yarn
- Viscose Staple Fiber
Which regions are prominent in the Viscose Fiber Market?
The leading regions in the Viscose Fiber market include:
- North America (United States, Canada, and Mexico)
- Europe (Germany, United Kingdom, France, Italy, Russia, Turkey, etc.)
- Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, and Vietnam)
- South America (Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, etc.)
- Middle East and Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria, and South Africa)