What is Airlaid nonwoven?
Airlaid nonwoven is a type of fabric made using the airlaid process, which involves the dispersion of fibers into an air stream and then collecting them on a moving belt or screen to form a web. This process is especially effective for creating fabrics with high absorbency, softness, and uniformity. Here’s a detailed look at airlaid nonwoven fabrics:
Production Process
- Fiber Selection:
- Types of Fibers: Airlaid nonwovens typically use short fibers, including natural fibers (like wood pulp, cotton) and synthetic fibers (like polyester, polypropylene, bicomponent fibers).
- Blending: Fibers are often blended to achieve specific characteristics such as absorbency, strength, and softness.
- Fiber Preparation:
- Opening and Blending: Fibers are opened and blended to ensure a uniform mixture.
- Defibration: For wood pulp, the fibers are defibrated into individual pulp fibers before being dispersed into the air stream.
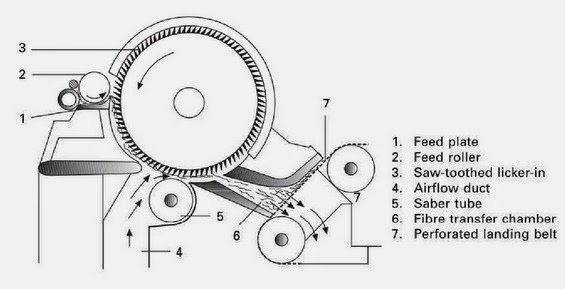
- Airlaying:
- Fiber Dispersion: Fibers are dispersed into an air stream to form a uniform cloud of fibers.
- Web Formation: The fiber cloud is directed onto a moving conveyor belt or perforated drum where the fibers settle and form a web. The vacuum underneath helps to hold the fibers in place.
- Web Consolidation: The loose web is then bonded to give it strength and stability. This can be done using different methods like thermal bonding, latex bonding, or through the use of bicomponent fibers that melt upon heating to bond the fibers together.
Characteristics of Airlaid Nonwovens
- High Absorbency: Excellent for applications requiring high liquid absorption and retention due to the high porosity and capillary action of the web structure.
- Softness: The process allows for the creation of very soft fabrics, making them suitable for hygiene and personal care products.
- Uniformity: The airlaying process ensures a uniform distribution of fibers, resulting in consistent fabric properties.
- Bulkiness: The fabrics can be bulky, providing cushioning and insulation properties.
- Customizability: Fiber types and bonding methods can be varied to tailor the fabric properties for specific applications.
Applications of Airlaid Nonwovens
- Hygiene Products:
- Disposable Diapers: Used in the absorbent core for high liquid retention.
- Sanitary Napkins and Pads: Provides absorbency and softness.
- Adult Incontinence Products: Ensures high absorbency and comfort.
- Wipes:
- Wet Wipes: Used for baby wipes, cleaning wipes, and personal care wipes due to their softness and absorbency.
- Dry Wipes: Suitable for industrial and household cleaning.
- Medical Products:
- Surgical Pads and Sponges: Used for their absorbency and softness.
- Medical Drapes and Gowns: Provides barrier properties and absorbency.
- Tabletop Products:
- Disposable Tablecloths and Napkins: Offers absorbency and a soft feel, making them ideal for food service.
- Industrial Applications:
- Oil Absorbents: Effective in absorbing oil and other hydrophobic liquids for spill containment.
- Filters: Used in air and liquid filtration systems due to their uniform structure and high absorbency.
Advantages of Airlaid Nonwovens
- High Absorbency: Suitable for products requiring quick and high liquid absorption.
- Softness and Bulk: Provides comfort and cushioning, ideal for hygiene and medical products.
- Uniformity: Ensures consistent performance across the fabric.
- Versatility: Can be tailored to meet specific needs by varying fibers and bonding methods.
Disadvantages of Airlaid Nonwovens
- Mechanical Strength: Generally, airlaid nonwovens have lower mechanical strength compared to other nonwovens like spunbond or needle punched fabrics, unless reinforced.
- Cost: Production can be more costly due to the complexity of the airlaying process and the types of fibers used.
Key Considerations
- Fiber Selection and Blending: The choice and blend of fibers affect the fabric’s absorbency, strength, and softness.
- Bonding Method: Different bonding techniques can significantly influence the final properties of the fabric, such as its strength and durability.
- Application Requirements: The specific needs of the end-use application will determine the appropriate fiber types, web formation techniques, and bonding methods.
Airlaid nonwovens are essential in many industries, particularly those requiring high absorbency, softness, and uniformity. Their versatility and customizable nature make them suitable for a wide range of applications from hygiene and medical products to industrial uses and consumer goods.
VNPOLYFIBER is pleased to supply China Airlaid Nonwoven products made from Bico PE/PET or PE/PP in combination with Fluff Pulp. We are committed to maintaining the highest standards of product quality, which has led to a high level of customer satisfaction with our Airlaid Nonwoven offerings. We carefully select qualified suppliers in China to provide competitive pricing for our customers globally.
Airlaid Nonwoven Fabric Made from Bico PE/PET or PE/PP and Fluff Pulp with the Following Key Characteristics:
Airlaid nonwoven fabric offers several advantages when compared to conventional wetlaid paper and tissue. It is characterized by its bulkiness, porosity, and softness, as well as excellent water absorption properties and high tensile strength, even in wet conditions. Its versatility allows for a wide range of applications.
If you are interested in a specific item, please contact us to request a Technical Data Sheet (TDS).
Product Specifications
– Width: 10cm – 180cm
– Basis Weight: 15gsm – 200gsm
– Spin Finish: Standard Hydrophilic
– Packaging: Jumbo roll or customized sizes
Applications of Airlaid Nonwovens
Food and Cooking
– Tabletop products (napkins, tablecloths, etc.)
– Meat pads
– Food wrappings
– Cooking paper
Personal Hygiene & Beauty
– Diapers and other incontinence products
– Pads (both wet and dry) for various uses
– Masks
– Oshibori towels
Medical
– Bed, pillow, and surgical sheets
– Surgical gowns, hats, and shoe covers
– Towels (both wet and dry)
– Washing gloves
Household & Industrial
– Filter elements
– Wipes (both wet and dry)
– Fluid absorbents
What is Air Through Bond Nonwoven?
Air-through bond nonwoven fabrics are a type of nonwoven fabric created through a thermal bonding process where hot air is used to bond the fibers together. This method is known for producing soft, bulky, and breathable fabrics, making it ideal for applications that require comfort and air permeability. Here’s an in-depth look at air-through bond nonwoven fabrics:
Components and Process
- Fiber Selection:
- Thermoplastic Fibers: Typically, polyester, polypropylene, or bicomponent fibers (fibers with a core of one polymer and a sheath of another polymer with a lower melting point) are used.
- Blending: Different fibers can be blended to achieve specific properties such as softness, strength, and thermal resistance.
- Web Formation:
- Carding: Fibers are opened, aligned, and layered into a web using carding machines.
- Air Laying: Fibers are dispersed in an air stream and deposited onto a moving conveyor belt to form a uniform web.
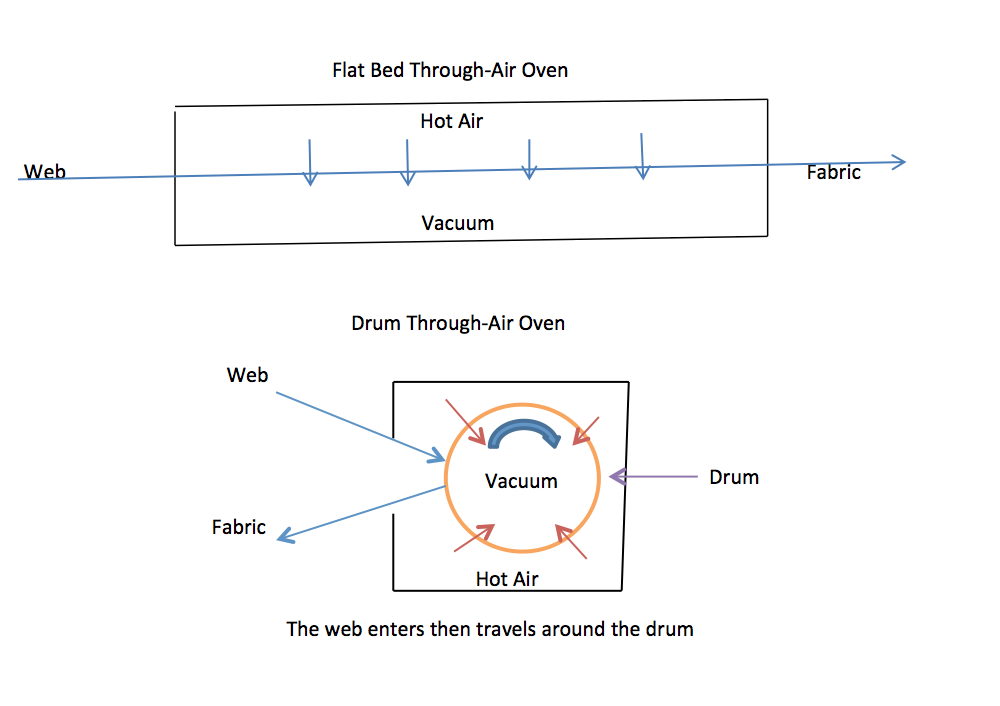
- Air-Through Bonding:
- Heat Application: The fiber web is passed through an oven or heated chamber where hot air is blown through the web. The temperature of the air is carefully controlled to melt the low melting point fibers (typically the sheath in bicomponent fibers) without affecting the higher melting point fibers (typically the core in bicomponent fibers).
- Cooling: As the web cools, the melted fibers solidify, bonding the fibers together at their contact points.
- Finishing:
- Cooling and Stabilization: The bonded web is cooled to stabilize the bonds and solidify the fabric structure.
- Additional Treatments: The fabric may undergo further processing like embossing, laminating, or chemical finishing to enhance specific properties.
Characteristics of Air-Through Bond Nonwovens
- Softness and Bulkiness: The air-through bonding process produces fabrics that are soft, bulky, and cushiony.
- Breathability: The open structure of the fabric allows for excellent air and moisture permeability.
- Uniformity: The process ensures a uniform fabric structure with consistent properties.
- Lightweight: The resulting fabric is lightweight, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
- Recyclability: Depending on the fibers used, air-through bond nonwovens can be recyclable.
Applications
- Hygiene Products:
- Diapers: Used in the top sheet and acquisition layer for their softness, bulkiness, and breathability.
- Sanitary Napkins: Provides comfort and absorbency in the top sheet and core.
- Medical Products:
- Disposable Medical Gowns and Drapes: Offers comfort and breathability for single-use medical garments.
- Surgical Masks: Used as the inner layer for its softness and breathability.
- Consumer Goods:
- Disposable Wipes: Used for baby wipes, facial wipes, and cleaning wipes due to their softness and absorbency.
- Home Textiles: Used in products like mattress covers, pillowcases, and furniture linings for their comfort and durability.
- Filtration:
- Air Filters: Used in HVAC systems and other air filtration applications for their breathability and filtration efficiency.
- Liquid Filters: Used in various liquid filtration systems where lightweight and breathable materials are needed.
- Automotive:
- Interior Linings: Used in car interiors for their softness and cushioning properties.
- Insulation: Provides thermal and acoustic insulation in vehicles.
- Agriculture:
- Crop Covers: Protects crops from environmental elements while allowing air and moisture to pass through.
Advantages of Air-Through Bond Nonwovens
- Softness and Comfort: The fabric is soft and comfortable, making it ideal for personal care and medical applications.
- Breathability: Excellent air and moisture permeability make it suitable for hygiene and filtration applications.
- Uniform Structure: Ensures consistent performance and quality.
- Lightweight and Bulky: Combines bulkiness for cushioning with a lightweight structure.
- Recyclability: Depending on the fibers used, it can be an environmentally friendly option.
Disadvantages of Air-Through Bond Nonwovens
- Lower Strength: Compared to other nonwoven bonding methods like spunbond or needle punch, air-through bond nonwovens may have lower tensile strength.
- Cost: The production process can be more expensive compared to other nonwoven processes due to the need for precise temperature control and specialized equipment.
- Heat Sensitivity: The fabric may not perform well in high-temperature applications due to the thermoplastic nature of the fibers.
Key Considerations
- Fiber Selection: The choice of fibers, especially the use of bicomponent fibers, is crucial for achieving the desired softness, strength, and thermal properties.
- Bonding Process: The air-through bonding process must be carefully controlled to ensure proper melting and bonding of fibers.
- End-Use Requirements: The specific needs of the application will dictate the selection of fibers, bonding methods, and any additional finishing processes.
Air-through bond nonwoven fabrics are known for their softness, breathability, and bulkiness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, particularly in the hygiene, medical, consumer goods, filtration, automotive, and agricultural sectors. Their unique properties and versatile production process make them a valuable material in various industries.